Porter’s Diamond Model analysis: Louis Vuitton and BMW
Learn about the business strategies used by Louis Vuitton and BMW from Porter’s Diamond Model analysis of these two successful and powerful organizations.
The Porter Diamond Model, also known as the Porter Diamond Theory of National Advantage is a business framework that describes a nation’s competitive advantage in the international market.
The model also highlights four factors that companies looking to expand their business internationally can take advantage of to achieve competitiveness in the market.
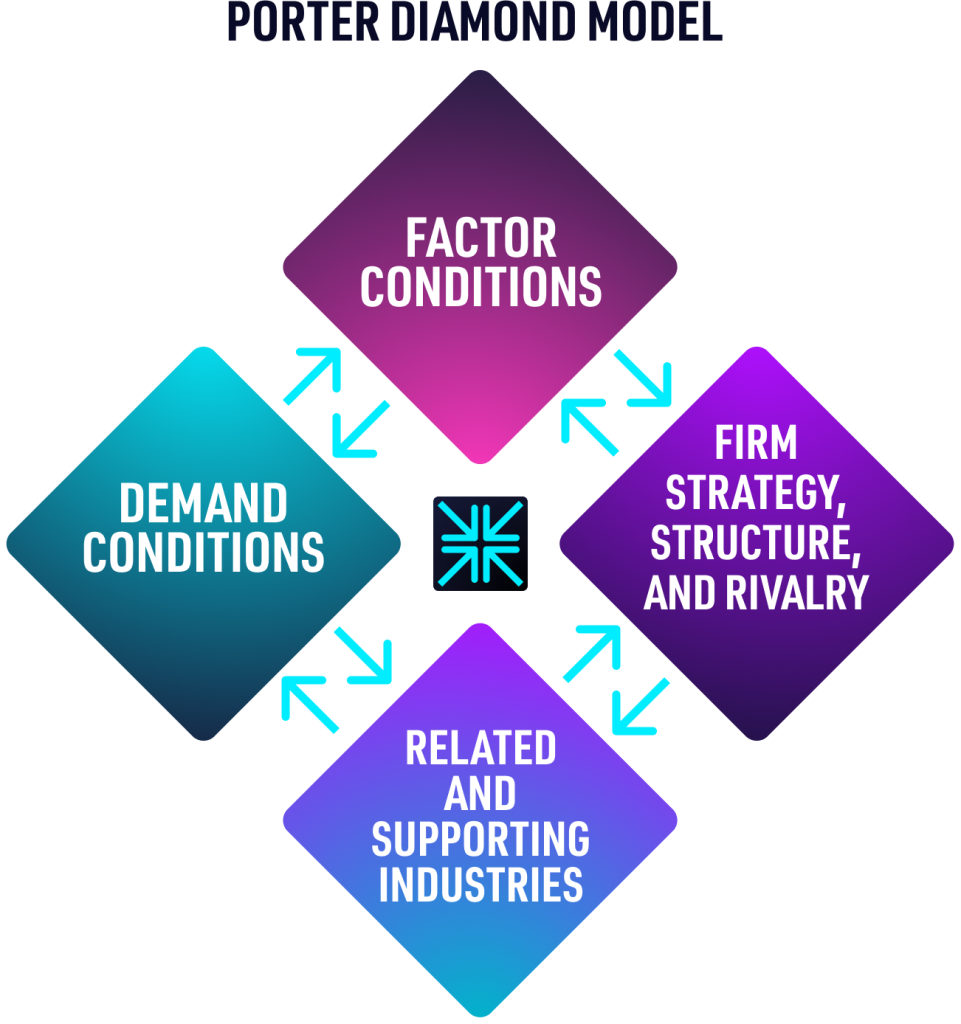
The Porter Diamond Model includes 4 attributes
The Porter Diamond Model analyzes a nation’s advantage against four broad attributes that each nation establishes and operates for its industries:
1.Factor Conditions
This attribute defines the nation’s position in factors of production, such as labour, land, natural resources, capital or infrastructure, necessary to compete in a given industry.
2. Demand Conditions
The second attribute of the Porter Diamond Model refers to the nature of home-market demand for the industry’s product or service.
3. Related and Supporting Industries
This attribute reveals the presence or absence in the nation of supplier industries and other related industries that are internationally competitive.
4. Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry
The Firm strategy, structure and rivalry attribute highlights the conditions in the nation governing how companies are created, organized, and managed, as well as the nature of the domestic competition.
For in-depth information on Porter’s Diamond Model, check out this article!
Theoretical knowledge is good but it’s only the starting point. Analyzing real-life examples is the best way to learn about a new business framework or model. It helps you put things in perspective.
For the purpose of this article, let’s look at two global brands and how the Porter Diamond Model is applied to them: Louis Vuitton and BMW.
Porter’s Diamond Model Analysis of Louis Vuitton

With a brand value of over $51 million in 2020, Louis Vuitton is the most valuable luxury brand in the world.
France is the company’s home base but since its inception more than 150 years ago, Louis Vuitton has expanded in 50 countries and has a retail network of over 4,910 stores worldwide.
What is the secret of Louis Vuitton’s success? Read Louis Vuitton: The story behind the brand.
Louis Vuitton: Factor and demand conditions
When you think of luxury, you think of France.
France is the world’s capital for luxury goods, haute-couture fashion, cosmetics, perfumes and accessories and the home for famous international houses such as Chanel, Dior, Givenchy, L’Oreal, Clarins, Lancome, Hermes, Celine, Louis Vuitton etc.
It’s not by chance that France has such a strong cluster of luxury brands.
The country’s luxury goods industry has a long history which began more than 500 years ago.
Eight hundred years ago, France was Europe’s silk centre with a booming silk industry.
King Louis XIV, the country’s most fashionable royalty recognized the importance of luxury goods to the national economy. Under his leadership, the country developed a powerful textile industry which in turn boosted trading and the country’s infrastructure.
Fast forward to the 21st century, France is synonymous with high fashion and luxury goods.
The fashion and luxury goods industry has a direct turnover of €150 billion. The share of French GDP generated by fashion is 2.7%. There are 1 million jobs in the fashion industry (source). The workforce in the industry is highly skilled. Experienced craftsmen or seamstresses sometimes receive an 18-month to 2-year training.
France was the perfect country for Louis Vuitton to be born in. The country provided the luxury brand with perfect factor conditions.
The French are known for their good taste and high fashion style so the brand had to work hard and innovate to meet the needs of such demanding customers (demand conditions).
This, in turn, helped them expand internationally and retain their competitive advantages.
With 37% of global sales, the Asian market is Louis Vuitton’s biggest revenue source.
Surveys show that 92% of Japanese women own a Louis Vuitton handbag and sales in China rose by more than 50% and in August last year when the brand reported record sales at its largest store in Shanghai.
Louis Vuitton: Related and Supporting Industries
The country also ranks high in the Related and Supporting Industries attribute for the luxury goods industry.
The industry’s development has been in close relationship with many subsectors such as textile and apparel, garments and embellishments, and sewing machinery. It’s an ecosystem whose members pressured each other to improve and innovate for mutual benefit.
Louis Vuitton: Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry
In France, the luxury goods industry is highly competitive.
With pressure from competitors, online sales increase and technology disruption, Louis Vuitton’s business strategy is to grow through acquisitions.
The brand is part of LVMH, the world’s largest conglomerate which came to be in 1987 when Louis Vuitton merged with champagne and cognac producer Moët Hennessy.
Over a period of 34 years, LVMH acquired more than 70 famous luxury brands. The latest acquisition is Tiffany & Co.
Porter’s Diamond Model Analysis of BMW
BMW: Factor and demand conditions
Germany played a major role in the history of the automotive industry.
It was Karl Benz, a German mechanical engineer who designed and, in 1885, built the world’s first practical automobile to be powered by an internal-combustion engine. Today, Germany is renowned for its powerful and innovative cars.
The largest industry sector in Germany is the automotive industry. Vehicles make up almost 17% of total exports.
The automobile industry generated roughly 426 billion euros in total sales in 2018.
With 882,000 manufacturing jobs in the automotive industry, Germany ranks first among European countries.
The country is a primary location for innovative car manufacturers and suppliers and is home to powerful brands such as BMW, Audi, Volkswagen, Mercedes etc.
One of the factors underlying German success is that the workforce is created. German students benefit from the country’s dual system of education where they combine vocational education with apprenticeships. This type of education supplies the country with a steady flow of highly skilled workers.
The German automotive industry benefits from a strong industrial core, first-class infrastructure, a highly-skilled workforce and cutting-edge research and development.
BMW has become a prestige global brand, operating 31 plants in 14 countries, including the largest car manufacturing plant in the world.
BMW has taken advantage of the factor conditions provided by the country. Ranked 2019’s 3rd most valuable car brand in the world, the company didn’t start as a car manufacturer, but as an aircraft engine manufacturer.
The brand’s success relies on its outstanding car design, technological innovation and workforce.
As the Porter Diamond Model recommends, the brand grows its own workforce. The BMW Manufacturer-Specific Advanced Training (MSAT) program provides students with extensive training on BMW vehicles thus preparing them to work for the company.
BMW: Related and Supporting Industries
BMW cars are high-quality automobiles.
The brand carefully selects suppliers in subsectors of the automotive industry such as parts and components, heating, ventilation, air conditioning, electronics etc. BMW depends upon a network of over 100 auto parts suppliers from all over the globe, though approximately 50% of its suppliers are either located in Germany or are subsidiaries of German-based companies (source).
BMW: Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry
BMW faces tough competition both domestically and internationally.
The company’s competitors are legacy brands much like itself.
On the local market, car automakers differentiate themselves through brand positioning.
In recent years, German car manufacturers have been struggling to adapt to new technological challenges (car connectivity, e-mobility), environmental challenges (green technology) and new entrants such as Tesla.
To stay ahead of the competition, BMW is using a competitive strategy which builds on market relevance, competitive services and research and development.
And it continues to make cars that consumers can emotionally relate to.
Attend the BUSINESS STRATEGY MASTERCLASS, on October 27 and learn future-proof business strategies for your organization from Costas Markides, Professor of Strategy & Entrepreneurship at London Business School.
Limited number of seats. Get your tickets today!

Achieve competitive advantage with the Porter Diamond Model
Looking to achieve a competitive advantage in international markets? Apply the Porter Diamond Model!
On this page:
- What is the Porter Diamond Model?
- What are the four attributes discussed in Porter’s Diamond Model (with examples)?
- How do you use Porter’s Diamond?
1. What is the Porter Diamond Model?
The Porter Diamond Model, also known as the Porter Diamond Theory of National Advantage is a business framework that describes a nation’s competitive advantage in the international market.
The Porter Diamond Model also refers to innovation and why certain companies based in certain nations are capable of consistent innovation.
The model was created by economist and researcher Michael Porter whose expertise focuses on market competition and company strategy.
If you follow this blog, you are already familiar with Mr Porter and his earlier business framework, Porter’s 5 Forces.
2. What are the 4 attributes discussed in Porter’s Diamond Model?
The Porter Diamond Model analyzes a nation’s advantage against four broad attributes that each nation establishes and operates for its industries:
- Factor Conditions
- Demand Conditions
- Related and Supporting Industries
- Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry
Porter Diamond Model – Attribute #1 – Factor Conditions
This attribute defines the nation’s position in factors of production, such as labour, land, natural resources, capital or infrastructure, necessary to compete in a given industry.
It is worth noting that these factors are not inherited, but created.
According to the Porter Diamond Model, having a general workforce that is high school or even college-educated doesn’t constitute a competitive advantage.
To become competitive in the industry, a nation’s workforce must be highly specialized in an industry’s particular needs.

In Germany, the largest industry sector is the automotive industry.
The country is a primary location for innovative car manufacturers and suppliers and home to powerful car manufacturers such as BMW, Audi, Volkswagen, Mercedes etc.
The German automotive industry benefits from a strong industrial core, first-class infrastructure, a highly-skilled workforce and cutting edge research and development.
One of the factors underlying the German success is that the workforce is created. German students benefit from the country’s dual system of education where they combine vocational education with apprenticeships. This type of education supplies the country with a steady flow of highly skilled workers.
Nations succeed in industries where they are particularly good at factor creation. Competitive advantage results from the presence of world-class institutions that first create specialized factors and then continually work to upgrade them.
Michael Porter
Porter Diamond Model – Attribute #2 – Demand Conditions
The second attribute of the Porter Diamond Model refers to the nature of home-market demand for the industry’s product or service.
Demand conditions include the nature of domestic buyers and of emerging buyer needs.
In a nation where the domestic buyers are the world’s most sophisticated and demanding buyers for the product or service, the nation’s companies gain competitive advantage.
Demanding domestic buyers pressure companies to improve, innovate and upgrade their products. Thus preparing them to rise to the challenges of buyers in other nations.

Amazon is leading the eCommerce industry in the US and worldwide.
What makes Amazon so successful on both domestic and international markets? The company’s focus on customer satisfaction.
Every product and service developed by Amazon is designed to delight customers and build a system around true customer obsession. Read this article to learn more.

Denmark is the world’s leading country in cleantech.
40% of Denmark’s total power consumption is covered by wind turbines with the goal of raising to 55% by 2030.
Everyone in Denmark is working to achieve this goal: the government, local authorities, corporations and the public.
Denmark’s energy transformation started in the 1970s when the country faced a severe energy crisis which left Denmark crippled. In just a few decades, the country veered from fossil fuels to clean energy.
Today Denmark holds exceptional cleantech opportunities with a collaborative business environment, government support and attractive framework conditions.
Nations gain competitive advantage in industries where the home demand gives their companies a clearer or earlier picture of emerging buyer needs, and where demanding buyers pressure companies to innovate faster and achieve more sophisticated competitive advantages than their foreign rivals.
Michael Porter
Porter Diamond Model – Attribute #3 – Related and Supporting Industries
This attribute reveals the presence or absence in the nation of supplier industries and other related industries that are internationally competitive.
Internationally competitive home-based suppliers create advantages by delivering the most cost-effective inputs in an efficient, early, rapid, and sometimes preferential way. Developing a close relationship between your company and its home-based suppliers is mutually beneficial.

South Korea is the world’s largest producer of semiconductors. The semiconductors industry is a supplier for a wide range of other tech-oriented industries such as smartphone manufacturers, CCTV cameras, car manufacturers etc.
The country is home to leading high-tech companies such as Samsung, Hyundai or LG.
Porter Diamond Model – Attribute #4 – Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry
The Firm strategy, structure and rivalry attribute highlights the conditions in the nation governing how companies are created, organized, and managed, as well as the nature of the domestic rivalry.

In Italy, for example, successful companies are often small or medium-sized family-run companies.

In China, 85% of enterprises are state-owned and lacking in market flexibility.

In the United Arab Emirates, the law required foreign companies to set up their businesses in partnership with an Emirati sponsor. Starting in November 2020, the government changed the law to allow 100% foreign ownership of businesses.
These four attributes make up the foundation upon which nations build their business environment. This environment determines how companies are born and how they learn to compete.
3. How do you use Porter’s Diamond?
Is your company looking to achieve international competitive success?
Here are 6 main insights provided by the Porter Diamond model:
- availability of resources necessary for competitive advantage in the industry of your choice;
- availability of skills necessary for competitive advantage in the industry of your choice;
- information that shapes the opportunities;
- directions in which companies deploy their resources and skills;
- goals of the owners, managers, and individuals in companies;
- the pressures on companies to invest and innovate.
If your company is planning to achieve a competitive advantage in the industry, investigate to which extent the national environment supports the rapid accumulation of specialized assets and skills.
Or whether or not the national environment affords better ongoing information and insight into product and process needs.
Does the national environment pressure companies to innovate and invest?
If the answers to these questions are affirmative, then your company could gain a competitive advantage and upgrade those advantages over time.
Join the Conversation
We’d love to hear what you have to say.
Get in touch with us on our LinkedIn Page, Facebook Page, Twitter or TikTok.
The story behind the brand: Louis Vuitton
Louis Vuitton is leading the global luxury goods industry. Here is the brand’s story.
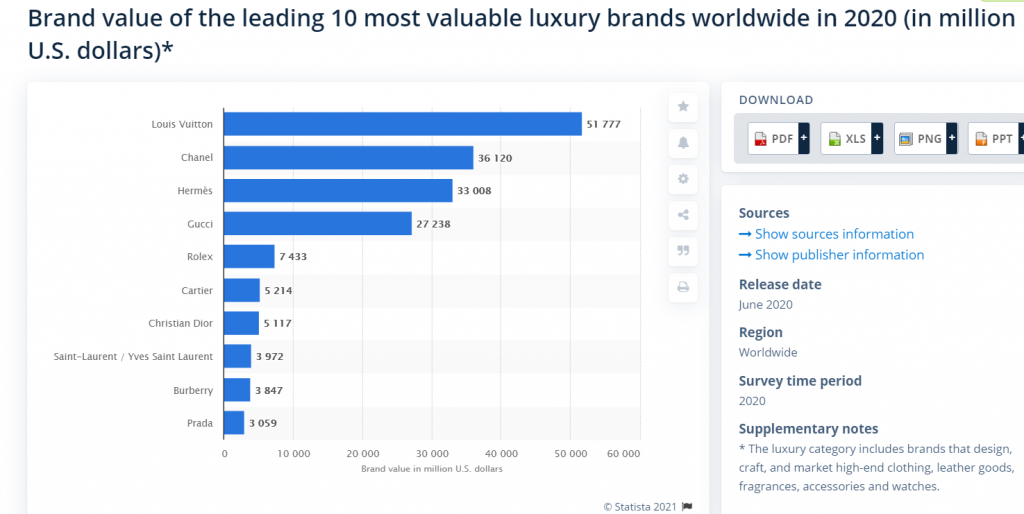
Source: Statista
Louis Vuitton – the leader of the global luxury goods industry
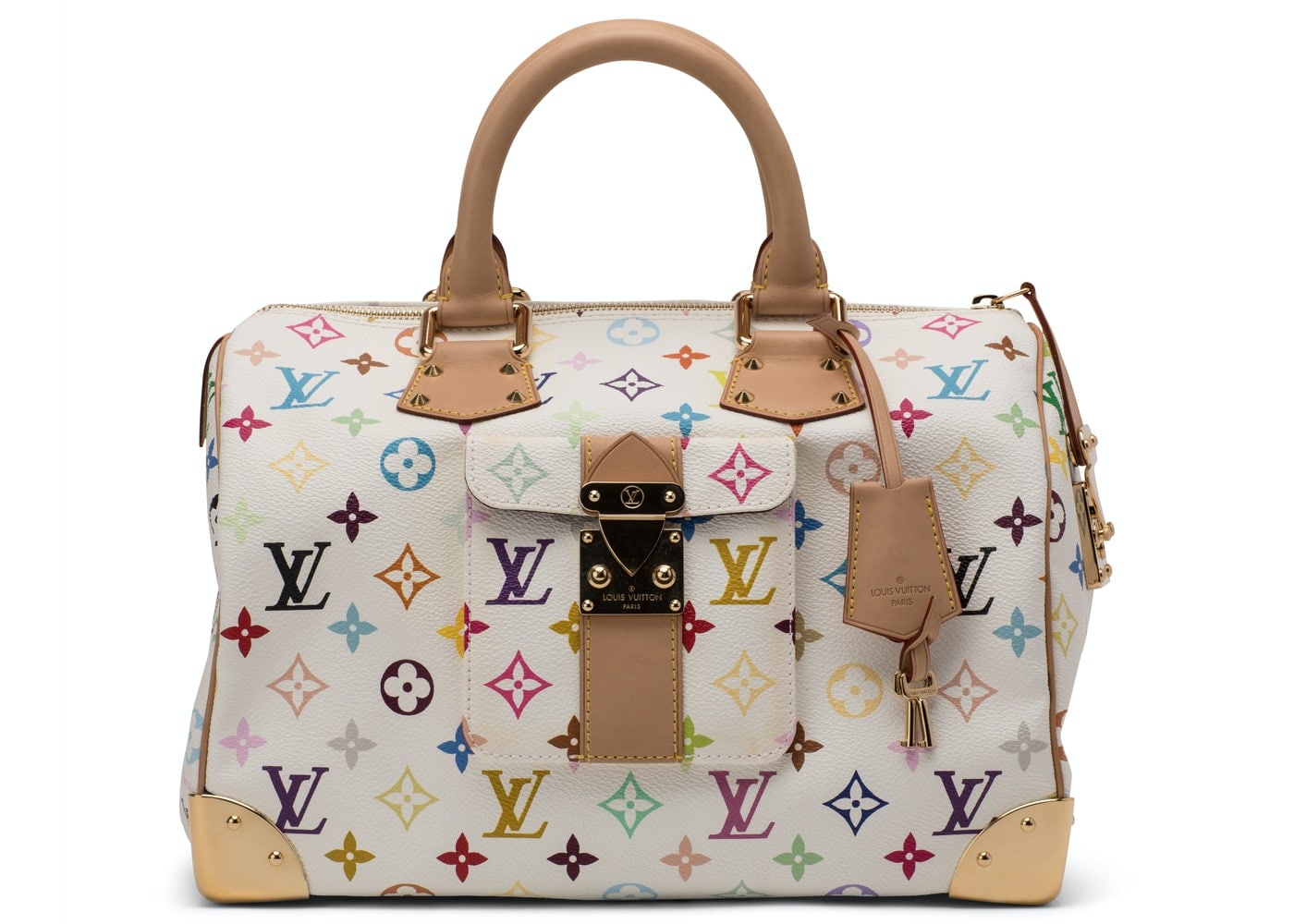
With a brand value of over $51 billion in 2020, Louis Vuitton is the most valuable luxury brand in the world.
The company operates in 50 countries, has a retail network of 5003 stores worldwide and earned 44,7 billion euros in revenue for 2020.
One of its latest flagship stores was inaugurated in February last year, in Japan. The Louis Vuitton Maison Osaka Midosuji is a stunningly designed store which hosts Café V, the first-ever Louis Vuitton café, as well as its first restaurant, Sugalabo V, offering cuisine with Franco-Japanese influences.
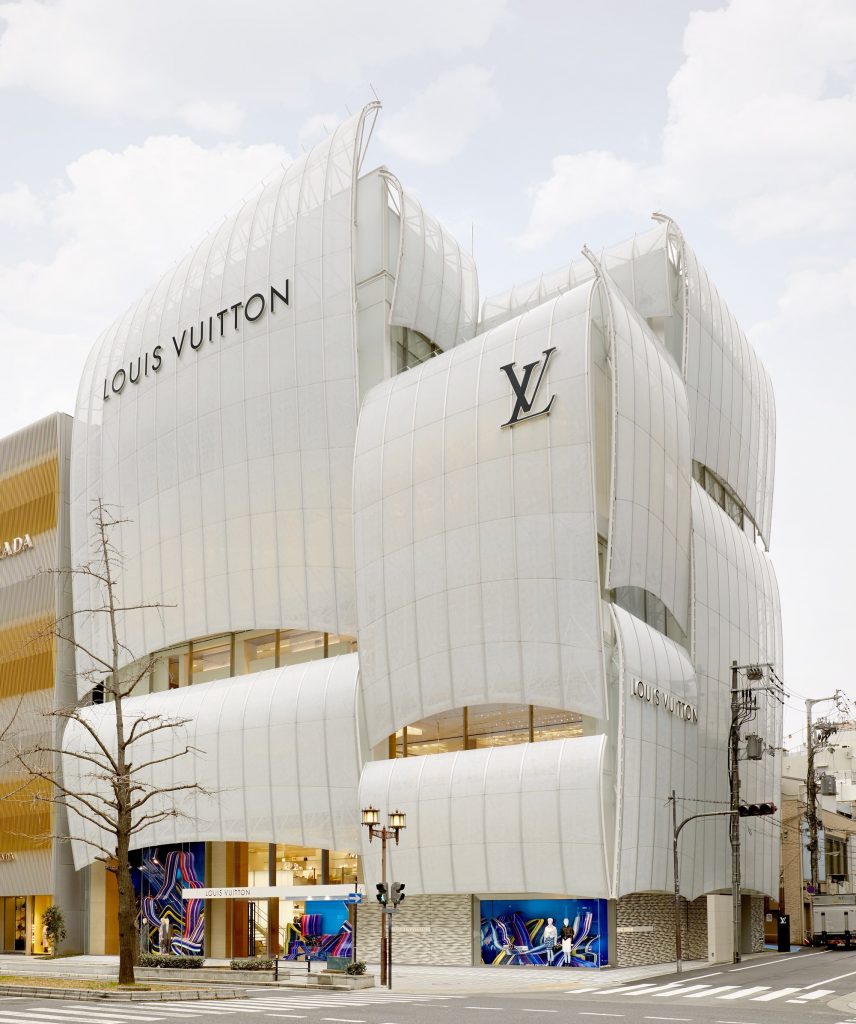

Louis Vuitton Maison Osaka Midosuji in Japan
Business in Asia is booming for Louis Vuitton and other luxury brands. Countries such as Japan, China, India and Singapore have welcomed Louis Vuitton.
The brand opened its first store in Japan in 1918 and up until the early 2000s, the Country of the Rising Sun accounted for more than half of its sales.
Surveys show that 92% of Japanese women own a Louis Vuitton handbag.

LV CRAFTY: MONOGRAM EMPREINTE
China is another success story for the brand. The French leader entered the Chinese market in 1992 and has seen a steady rise in its sales there. How else to show success and status than to flaunt an elegant Louis Vuitton bag on your arm?
Last year, sales in mainland China rose by more than 50% and in August, the brand reported record sales of US$ 22 million at its largest store in Shanghai.
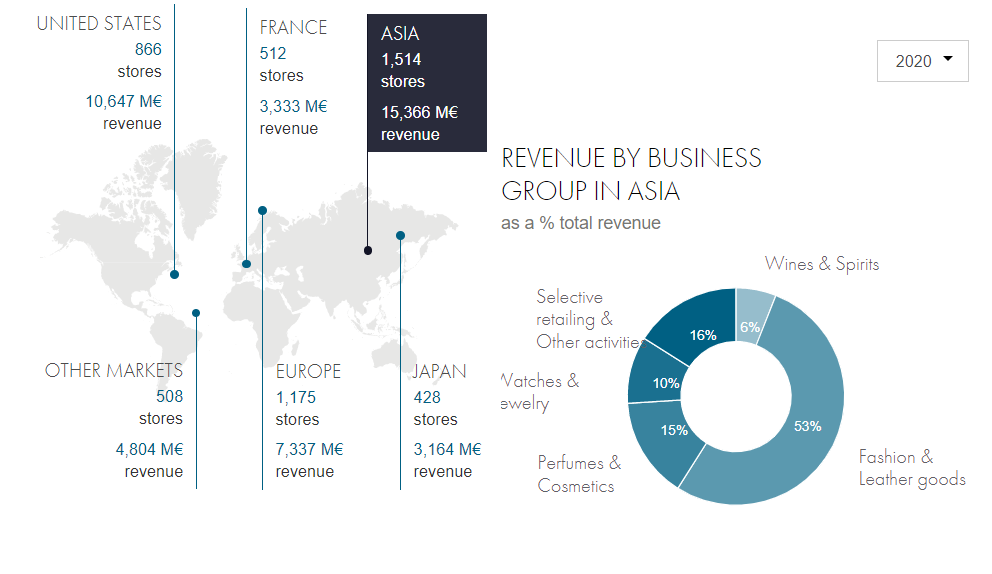
source: lvmh.com
Louis Vuitton, the man – craftsman and innovator
Louis Vuitton was born to a working-class family in eastern France. When he was 16 he left his family and came to Paris in search of a better life.
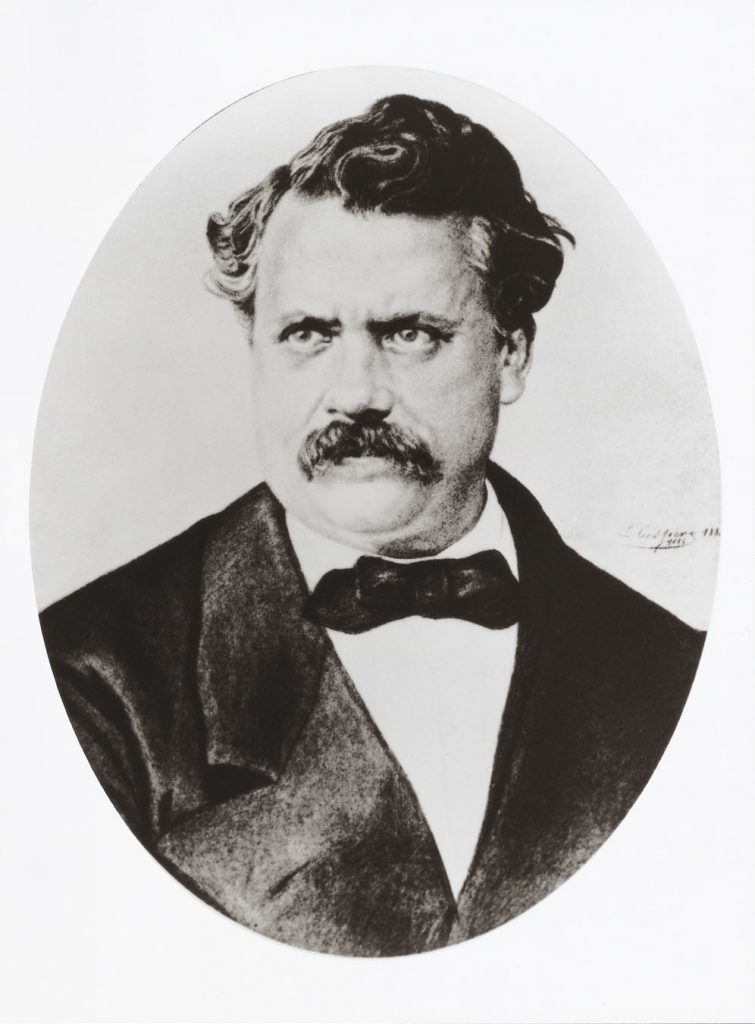

Louis Vuitton
Louis arrived in a thriving city in the midst of industrialization. Trains were becoming the preferred means of transportation for people. And with frequent travellers came the need for more durable travel pieces which could both protect travellers’ belongings and withstand longer journeys.
Thus the young Louis started apprenticing for Monsieur Maréchal, a successful box-maker and packer.
Under the guidance of the trunk-master, Louis became a valued craftsman and seventeen years later, he opened his own shop in Paris – he was 33.
He soon introduced his first innovation. At the time, trunks had rounded tops to allow for water to run off. The downturn – stowage was inconvenient. He introduced the flat-top trunk which was easily stacked. He also made the trunks waterproof by using leather.
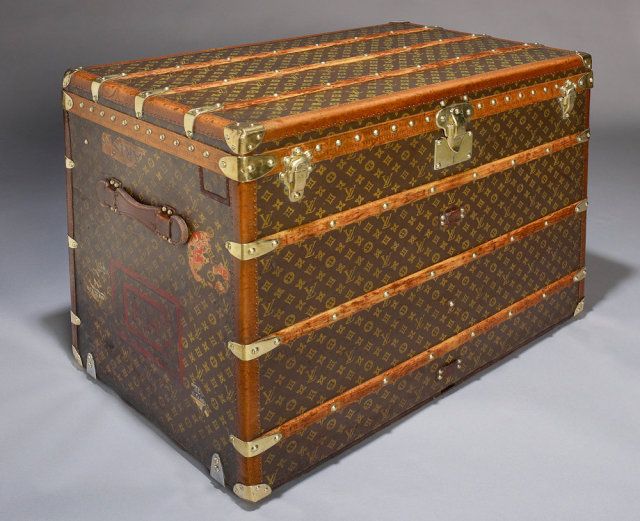

Louis Vuitton trunk cca 1920
Georges Vuitton – developing the brand
When Louis passed away at 70, his son, Georges took his place at the helm of the company.
His father established the company, but Georges developed it into a global brand.
The travel trunks made by the Vuitton company were sturdy and luxurious looking which attracted burglars. With the goal to protect the traveller’s belongings from burglars, Georges designed a new lock for the brand’s trunks.
After years of development, the locking system, which is still used today, proved revolutionary, making the Vuitton trunks impossible to be picked by burglars.
In 1896, to honour his father’s legacy, Georges introduced the first LV monogram. The monogram was patterned with LVs, quatrefoils, and flowers.

Under Georges’ leadership, the brand became highly successful nurturing an elite clientele among royalty, celebrities and the rich.
From Louis Vuitton, the company to LVMH, the luxury brand powerhouse
The LVMH conglomerate came to be in 1987 when Louis Vuitton merged with champagne and cognac producer Moët Hennessy.
In the following years, LVMH acquired over 70 brands becoming the world’s largest and most valuable luxury goods conglomerate.
Here are some of the most famous luxury brands that LVMH has acquired so far:
Dom Pérignon (vintage Champagne)
Givenchy (fashion, cosmetics and fragrances)
Guerlain (perfume and cosmetics)
Celine (ready-to-wear and leather luxury goods)
Loewe (ready-to-wear and leather luxury goods)
Marc Jacobs (fashion)
Sephora (multinational beauty chain)
TAG Heuer (luxury watch)
Bulgari (jewellery)
Christian Dior (fashion, cosmetics and fragrances)
Tiffany & Co. (jewellery)
Louis Vuitton business strategy for success – 3 pillars
1. Exclusivity
Louis Vuitton is a luxury brand. Luxury means exclusivity.
As a luxury brand, Louis Vuitton never hosts any sales. You can either afford a Louis Vuitton bag or you don’t.
Discounted prices are not part of the brand’s strategy. The products are sold exclusively in Louis Vuitton stores and through Louis Vuitton official website.
If you come across a Louis Vuitton bag on eBay, it’s most certainly a fake.
According to the latest estimations, Louis Vuitton is the most counterfeited brand in the world.
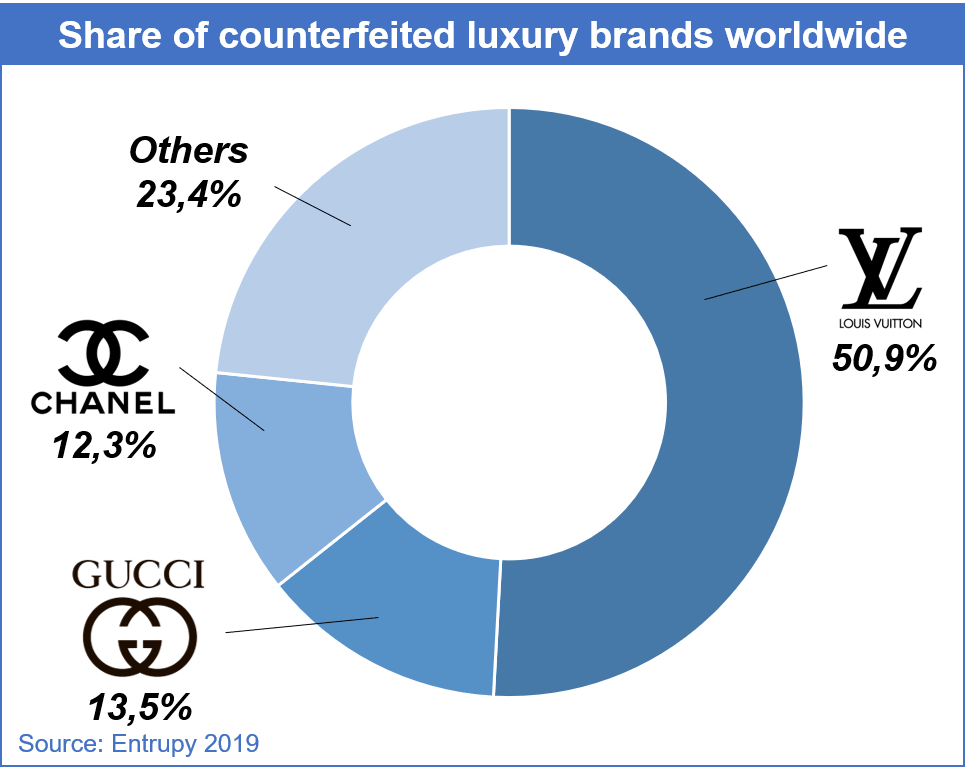
Nevertheless, an authentic Louis Vuitton bag is always in high demand. Renowned auction houses like Barnebys and Sotheby’s hold auctions of valuable Louis Vuitton bags and other products that bear the brand’s iconic monogram.
In 2020, one of the most expensive Louis Vuitton bag sold by Sotheby’s was the Louis Vuitton Matte Black Supreme Edition, in excellent condition. Its value was estimated between $6000-$10,000 and sold for $7500.

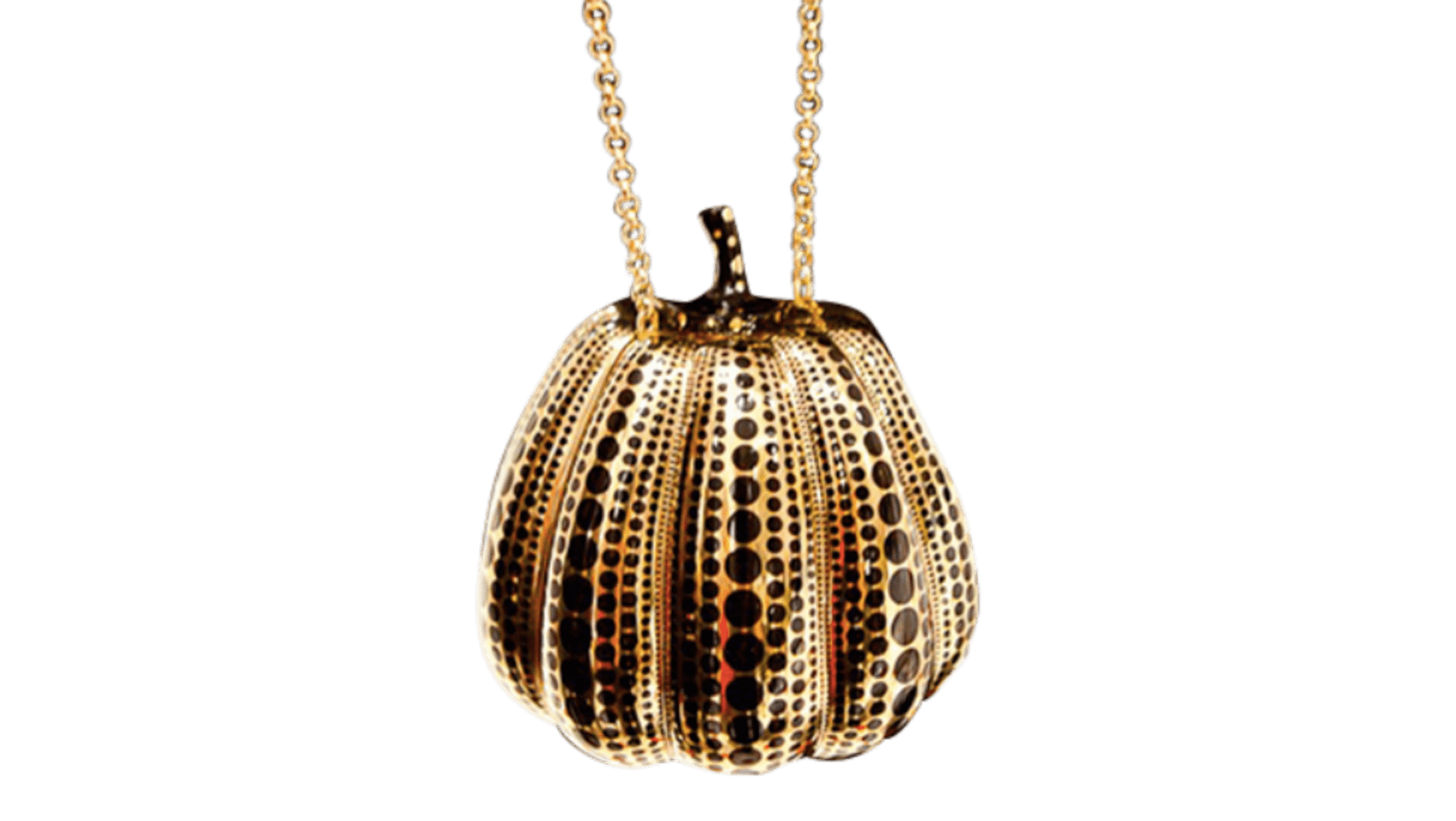
The most expensive Louis Vuitton lot sold by Sotheby’s last year was a Louis Vuitton trunk designed by famous Japanese designer Yayoi Kusama, aka ‘the princess of polka dots’. The trunk was estimated between 80,000 – 120,000 EUR and sold for 239,400 EUR, almost twice the highest estimate.
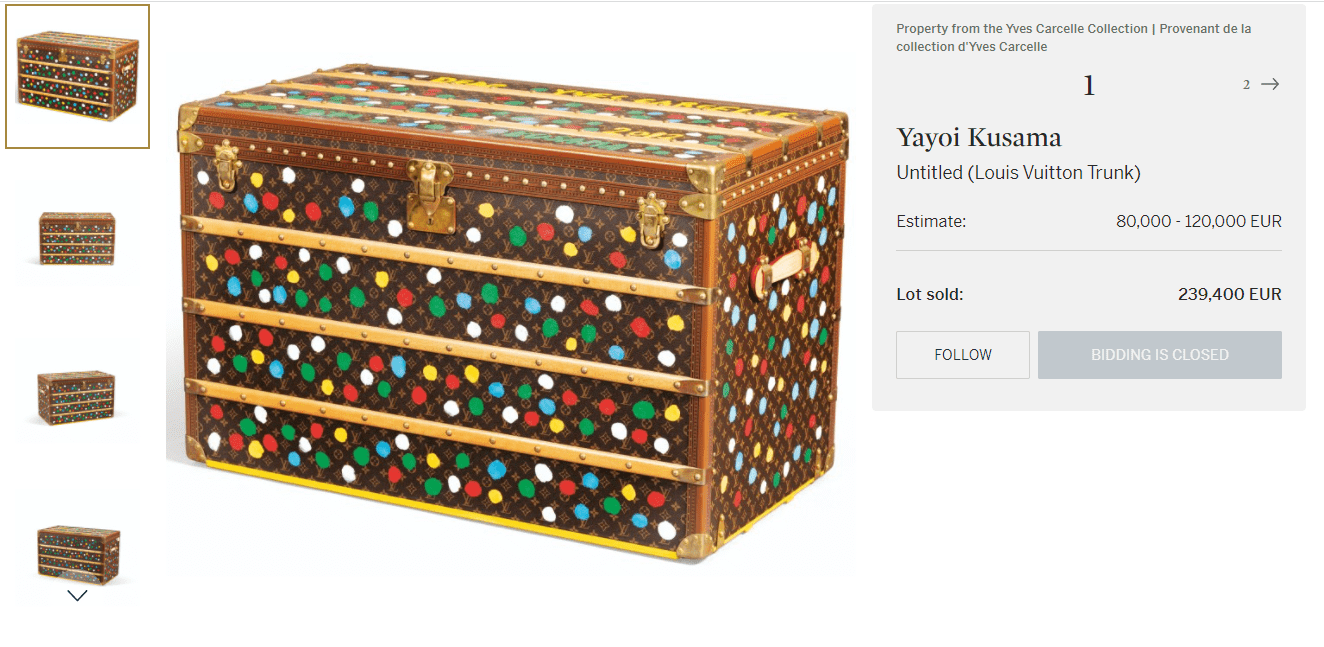
The most expensive Louis Vuitton bag ever to be sold in a store is the special edition Pumpkin Minaudiere by the same Yayoi Kusama. The pumpkin-shaped clutch is embellished with Kusama’s trademark dots and was priced at $133,430.

2. Handmade quality
The handmade quality of products is one of the founding principles of the Louis Vuitton brand. It began 167 years ago and it continues today. The items are made in the company’s factories located in France by skilled workers who sometimes receive an 18-month to 2-year training.
In regards to authenticity, the brand states as follows:
Authentic Louis Vuitton bags are handmade from experienced craftsmen who take pride in producing impeccable products from only the finest and highest quality materials.
The brand is synonymous with luxury, exclusivity and high-quality which create high demand in the market for its products. That’s the reason why there are so many fakes.
How to spot a fake Louis Vuitton bag?
Here are 6 key features that you should look closely at as explained by an appraiser:
Stitching. Every stitch on a Louis Vuitton bag is symmetric, perfectly aligned, with no space in between two stitches and no overlapping stitches.
Heat stamp. The heat stamp has a specific font with big round O’s, it is crisp and every letter is clear.
Leather. The Louis Vuitton bags are made of the finest leather that ages very well.
Pattern symmetry. Louis Vuitton uses a single piece of canvas, but if they need to make the bag from two pieces, they will always make sure the pieces align perfectly and the pattern match.
Production code. Every bag has a production code inside, sometimes embossed on the leather or on the suede material.
Brass details. All brass details on a Louis Vuitton bag are marked with LV.
3. Creating Desire
LVMH CEO and billionaire Bernard Arnault once said when asked about the future of Louis Vuitton,
In our business, the most important word is desire, so we want to continue creating desire.
This is the goal of Louis Vuitton: to design a brand strategy centred around creating desire.
How does Louis Vuitton create desire?
The 167-year old brand creates desire through a combination of tradition and creative innovation.
It all begins with building a real culture of creativity. Louis Vuitton’s top management is always looking to bring new designers with fresh ideas and a unique vision.
They also work with design schools and hire trainees and young designers. In 2014, the brand launched the LVMH Fashion Prize which aims to support young fashion designers. The winner receives a 300,000 euro grant and personalized assistance in the development of his or her company. LVMH also rewards three young fashion design graduates, offering them the chance to spend a year with the creative team at one of the Group’s Houses.
Another source of creativity and innovation is design collaboration. Over the years, Louis Vuitton has collaborated with many talented designers among which the most remarkable were Japanese contemporary artist Takashi Murakami, the American skateboarding lifestyle brand Supreme, ‘the princess of polka dots’ Yayoi Kusama, punk couture pioneer designer Stephen Sprouse and Virgil Abloh, the so-called ‘millennial Karl Lagerfeld’.

Louis Vuitton x Stephen Sprouse

Louis Vuitton x Virgil Abloh

Louis Vuitton x Takashi Murakami
Join the Conversation
We’d love to hear what you have to say.
Get in touch with us on our LinkedIn Page, Facebook Page, Twitter or TikTok.
Hofstede’s cultural dimensions theory in advertising: KFC, BMW and Heineken
Hofstede’s cultural dimensions theory is a framework for measuring cultural dimensions from a global perspective. It is a useful business tool which provides insights for organizations looking to extend their business internationally.
I was curious to know if this tool is relevant in advertising so I selected three brands, KFC Singapore, BMW China and Heineken Italy and analyzed one ad for each brand.
To learn the Hofstede rankings of each country, I used this tool.
KFC Singapore
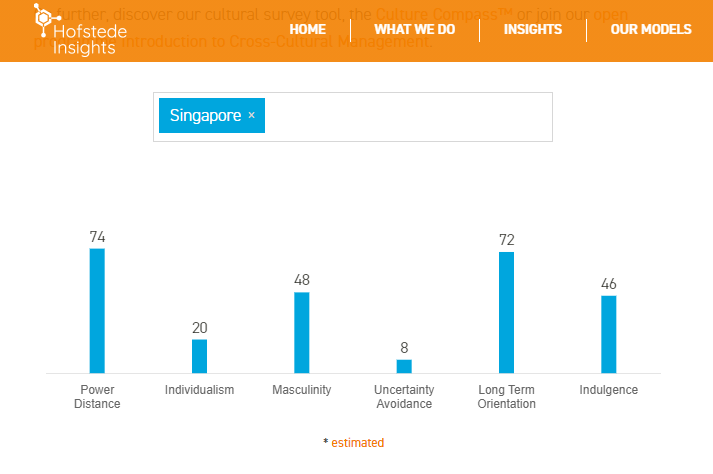
Power distance 74
Watching this ad by KFC Singapore, I see three cultural dimensions at play: power distance, individualism vs collectivism and masculinity vs femininity.
According to Hofstede’s theory estimations, Singapore ranks 74 at power distance. Power distance is the extent to which the less powerful members of organizations and institutions accept and expect that power is distributed unequally.
Singapore’s high score on this dimension indicates that it is a society that values hierarchy. This can be seen in the Singaporeans’ family meals customs which say that no one eats until the oldest member of the family lifts the spoon. In Singapore, older people are respected and listened to.
Individualism 20
The individualism vs collectivism dimension shows to which extent people feel independent or interdependent as members of larger communities. As you can see, Singapore ranks low in individualism which makes the society a collectivist one.
In the collectivist culture, family is at the heart of everything. A person views himself as a member of the family rather than an individual.
Masculinity 48
In regards to the masculinity dimension, Singapore ranks 48. Masculinity is the extent to which the use of force is endorsed socially.
Singapore’s rank tips the scale a little bit more to the feminine side. This means that conflicts are avoided and reaching a consensus is more important than being right.
What do we see in this ad?
We see a family preparing to eat together with the oldest, probably the grandmother sitting at the head of the table. As per tradition, everyone is inviting the grandmother to start eating. Although polite, what their invites do is repeatedly interrupt the hungry woman who doesn’t need convincing in front of a delicious bowl of KFC chicken. Because she doesn’t want to tell them off and ruin everyone’s good mood, she puts on a pair of headphones and starts eating with great pleasure.
BMW China
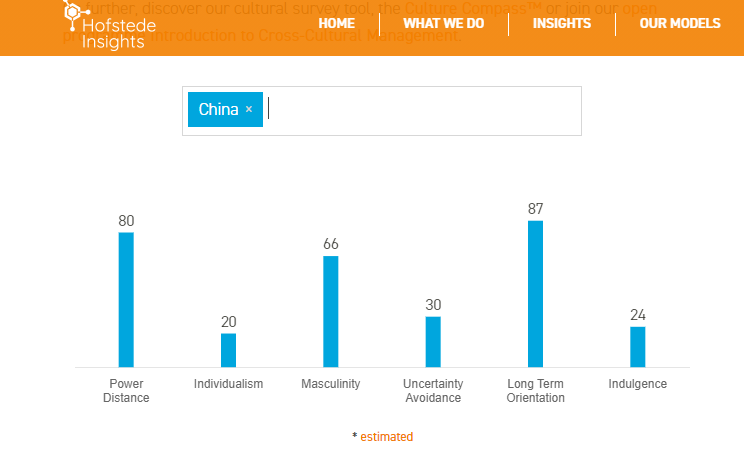
Power distance 80
This ad for the car manufacturer’s Chinese market pulls the strings on the viewer’s heart. It is longer than the average ad and uses this time to tell the story of a modern Chinese family with a hard-working white-collar father.
His son is trying to understand why his father is sometimes late to pick him up from kindergarten or even goes back to the office to work through the night. The only good reason he can think of is that his dad is a superhero and he gets wrapped up in doing superhero stuff.
China ranks very high in power distance. It is a country where subordinate-superior relationships tend to be polarized and can lead to power abuse by superiors.
We see this aspect of Chinese culture through the kid’s eyes: he imagines his father’s superiors as villains demanding him to dedicate his free time to the job and to making money because making money is more important than his son.
In his imagination, his father is fighting to overcome every obstacle that keeps him from coming home using every ability in his power: kung-fu strikes, negotiation or his bare fists. Like any other hero, he needs a sidekick to be successful and his BMW fulfils this role with flying colours.
Individualism 20
Chinese society ranks low in individualism. Although the ad focuses mainly on the kid, we can still see how important and how dedicated the father is to his son. He may be late, but he eventually shows up.
Masculinity 66
China is a masculine society where individuals are success-oriented and career-driven. And people have traditionally established roles.
As we can see in this ad, the mother is the child’s main caretaker and possibly a stay-at-home parent with the father having a well-paid job. Also, it’s not a coincidence that he is portrayed as a hero winning at everything he sets his mind to.
Heineken Italy
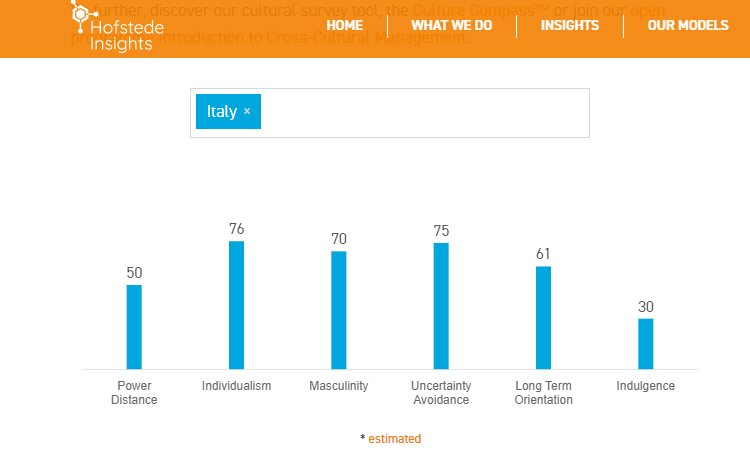
Masculinity 70
In this ad, we see Nico Rosberg, winner of the 2016 F1 World Championship and his father, Keke Rosberg, who also won the F1 World Championship, but 34 years earlier.
Competition is in their blood, both on the race track and in their father-son relationship also. Everything is a competition and winning is everything for this duo, from fishing the largest salmon to playing a game of tennis or throwing a paper ball into the trash can. And the loser gets to drive the car.
In the Behind the scenes video, Nico shares that to some extent, the ad reflects their relationship in real life. Playing a few games of tennis was a way for him and his father to spend time together.
Looking to expand your business into new markets?
Join BRAND MINDS 2023 and learn new strategies to create demand for your business from Renee Mauborgne, Bestselling Author of Blue Ocean Strategy.

Join the Conversation
We’d love to hear what you have to say.
Get in touch with us on our LinkedIn Page, Facebook Page, Twitter or TikTok.
What is Hofstede’s cultural dimensions theory? UK vs China, a comparison
Table of Contents
What is Hofstede’s cultural dimensions theory (definition)
Hofstede’s cultural dimensions theory is a framework for measuring cultural dimensions from a global perspective.
It is a useful business tool which provides insights for organizations looking to extend their business internationally.
With this framework, any organization planning to enter a market in a new country becomes aware of the cultural differences of that particular country.
What are the 6 dimensions of Hofstede’s theory?
Hofstede’s theory includes 6 cultural dimensions (source):
- Power distance index
- Individualism vs. collectivism
- Uncertainty avoidance
- Masculinity vs. femininity
- Long-term orientation vs. short-term orientation
- Indulgence vs. restraint
Hofstede’s dimension #1 – Power distance index
Power Distance is the extent to which the less powerful members of organizations and institutions (like the family) accept and expect that power is distributed unequally.
This dimension lies with the people at the bottom, not the people at the top. The perfect example of the power distance is illustrated in the family, in the relationship between children and parents.
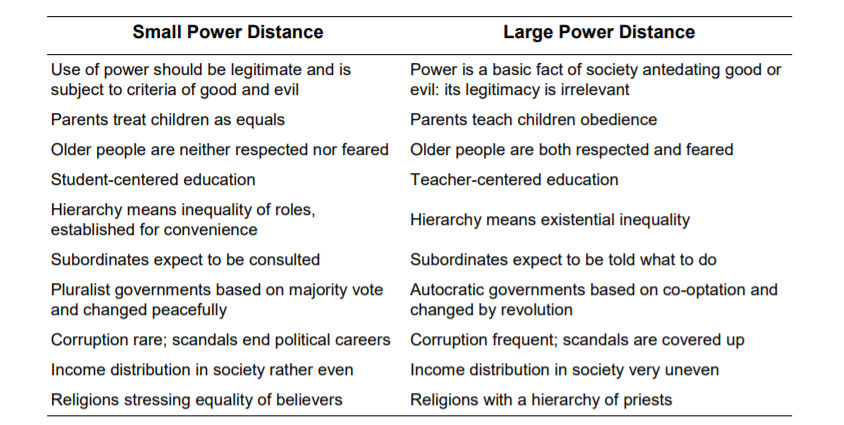
Hofstede’s dimension #2 – Individualism vs. collectivism
Individualism is the extent to which people feel independent, as opposed to being interdependent as members of larger communities.
Individualism means that individual choices and decisions are expected.
Collectivism means that everyone knows their place in life and society, which is determined socially.
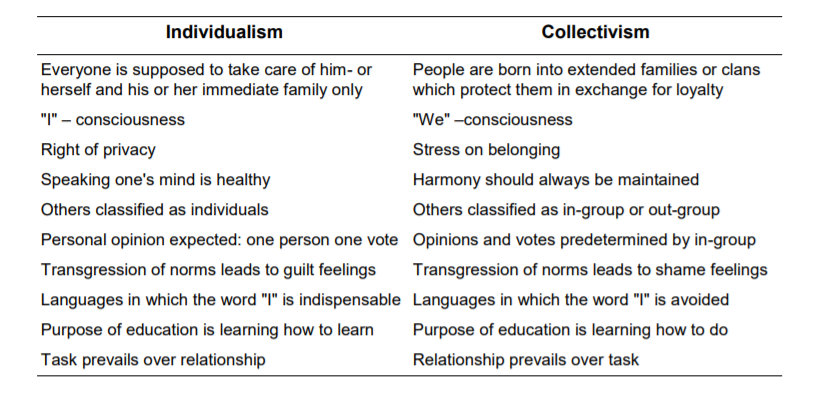
Hofstede’s dimension #3 – Uncertainty avoidance
Uncertainty avoidance deals with a society’s tolerance for uncertainty and ambiguity.
This dimension doesn’t refer to risk avoidance. It refers to the anxiety and distrust that people have in the face of the unknown and the absence of truth.
A high ranking of uncertainty avoidance illustrates people’s wish to have fixed habits and rituals and to know the truth.
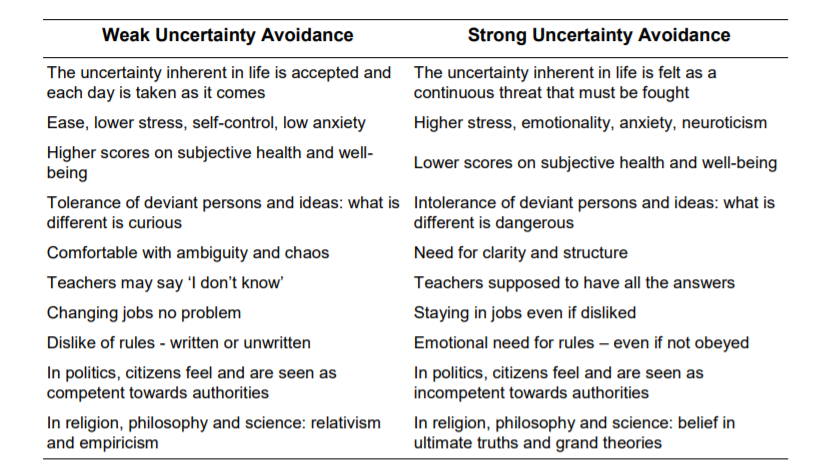
Hofstede’s dimension #4 – Masculinity vs. femininity
Masculinity is the extent to which the use of force is endorsed socially.
In a masculine society, men are expected to display specific behaviour traits like being and acting tough. Competition is at the heart of every activity and winning is important for both genders. There is a disconnect between men and women on an emotional level. In a feminine society, both genders are emotionally closer.
Competing is not so openly endorsed, and there is sympathy for the underdog.
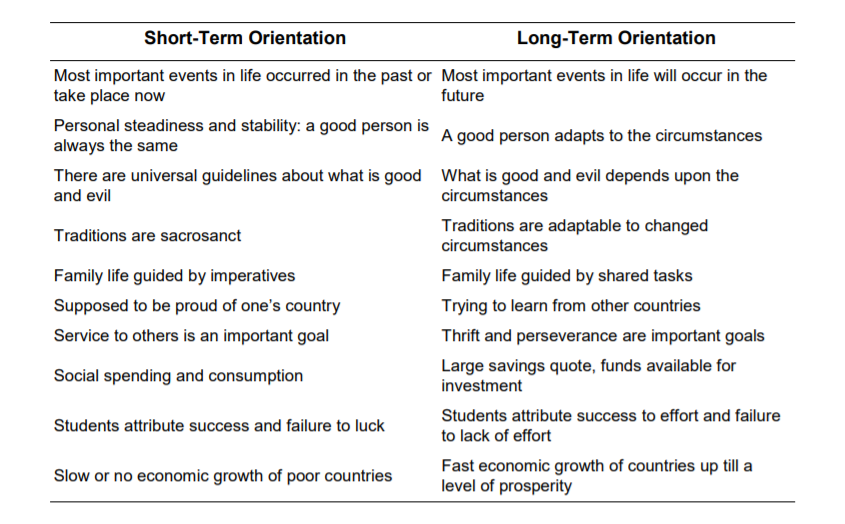
Hofstede’s dimension #5 – Long-term orientation vs. short-term orientation
The long-term orientation vs short-term orientation dimension is about change.
Cultures that believe the world keeps spinning, welcome change and look calmly towards the future. They know that preparing for the future is always needed. These cultures are long-term oriented and focus on technical and educational achievements.
Conversely, cultures that are short-term oriented place great emphasis on the past. They believe the world hasn’t changed much from the moment it was created. The past provides short-term oriented cultures with a blueprint for moral and social behaviour. It also influences their achievements.
Hofstede’s dimension #6 – Indulgence vs. restraint
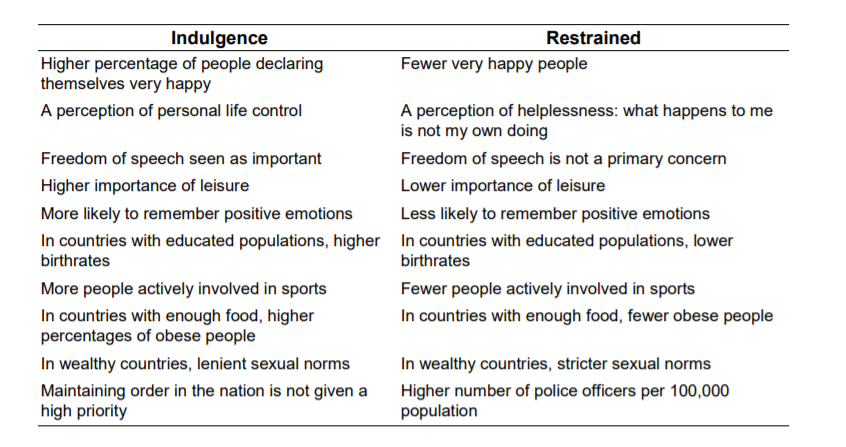
The sixth cultural dimension is about freedom and being able and allowed to have good things in life.
Indulgent cultures allow their people to fulfil their human basic pleasures and desires. People are free to enjoy their lives and have fun. They feel that they are in control of their lives.
Restraint cultures have strict social norms and regulations that suppress the fulfilment of needs and desires. People in restrained cultures feel less happy. They also feel that they cannot control what happens to them.
Who developed Hofstede’s cultural dimensions theory?
Hofstede’s cultural dimensions theory was developed by Dutch social psychologist Geert Hofstede while working at IBM International.
As a management trainer and manager of personnel research at IBM, Geert conducted over 100,000 employee opinion surveys in the subsidiaries of the company around the world.
At the time, his initiative produced one of the largest cross-national databases in existence.
The surveys revealed significant differences between cultures in other organizations, but the same answers by country.
Looking to organize the information in such a way that it produces valuable insights, he came up with four categories that he called cultural dimensions: power distance, individualism-collectivism, uncertainty avoidance, and masculinity-femininity.
He published his findings in his 1980 book Culture’s consequences: international differences in work-related values. In the following years, he added the fifth and sixth dimensions: long-term orientation and indulgence versus self-restraint.

Geert Hofstede is the pioneer of cross-cultural research.
His theory is one of the earliest and most popular frameworks for measuring cultural dimensions from a global perspective. In recognition of his work, Geert received many honorary awards and distinctions.
In 2011, he was made a Knight by order of Her Majesty Beatrix, Queen of the Netherlands.
What is Hofstede’s definition of culture?
Geert Hofstede’s definition of culture is Culture is the collective programming of the mind that distinguishes the members of one group or category of people from others.
Cultures range from micro (a family’s culture) to macro (a nation’s culture).
Culture can also refer to professional groups, religious groups, young or old etc.
What does a group of people believe about the nature of man or the future? What are the relationships between the members of the group? To which extent do people need rules and regulations?
Why is Hofstede’s theory important for your business?
Hofstede’s cultural dimensions theory is the third business framework presented in this blog (check the first two: Porter’s 5 forces and PESTEL).
This particular business tool is useful when planning to expand your business globally. If you wish to enter a new market in another country, analyze it first by applying Hofstede’s theory of cultural dimensions.
Is it a culture that respects the elderly? Use this piece of information when choosing the face of your marketing and PR communication or when choosing the influencers your company works with to raise brand awareness.
If the market you are trying to enter has a culture which equals being different from being dangerous then maybe it would be smart for your business to first educate the market about your brand or work on preventing your brand to be perceived negatively.
In feminine cultures, how will your business or brand be affected? If your brand supports freedom of speech, how will your brand perform in a restrained culture where freedom of speech is not a primary concern?
Hofstede’s cultural dimensions theory provides business executives with valuable insights that they can use to make informed decisions.
UK vs China, a comparison
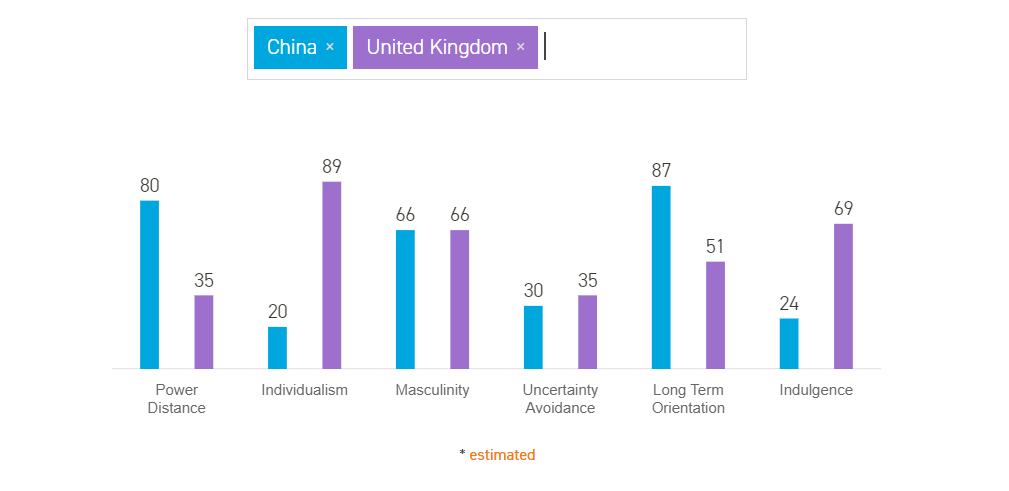
Power distance
UK 35% – a society that believes that inequalities amongst people should be minimized.
China 80% – a society that believes that inequalities amongst people are acceptable.
Individualism
UK 89% – a culture of people that are taught to think by themselves
China 20% – a highly collectivist culture where people act in the interests of the group and not necessarily of themselves.
Masculinity
UK 66% – a highly success-oriented and driven culture.
China 66% – success-oriented and driven, many Chinese will sacrifice family and leisure priorities to work.
Uncertainty avoidance
UK 35% – comfortable in ambiguous situations
China 30% – comfortable with ambiguity, are adaptable and entrepreneurial.
Long-term orientation
UK 51% – a society that equally values its own past while dealing with the challenges of the present and future
China 87% – a culture with a pragmatic orientation, that has the ability to easily adapt traditions to changed conditions
Indulgence
UK 69% – a culture that exhibits a willingness to realize their impulses and desires with regard to enjoying life and having fun.
China 24% – a restrained culture that doesn’t put much emphasis on leisure time and fulfilment of their desires.
Attend the BUSINESS STRATEGY MASTERCLASS, on October 27, and learn frameworks for creating a culture of continuous innovation from Costas Markides, Professor of Strategy & Entrepreneurship at London Business School.
Limited seats available. Get your tickets today!

Get your company back in growth model with Business Strategy for Top Executives
Are you looking to get your company back in growth model?
Then BRAND MINDS’ Business Strategy for Top Executives Masterclass is for you.
Get access now, the price goes up on February 1st!
The BRAND MINDS Business Strategy for Top Executives is a full-day premium learning experience
The Business Strategy for Top Executives Masterclass is hosted online on March the 23rd and provides participants with the opportunity to learn the principles of innovative companies.
The masterclass is a full-day premium learning experience delivered by Costas Markides, one of the world’s most renowned experts on strategy & innovation.
As the Professor of Strategy & Entrepreneurship at London Business School for the past thirty years, his expertise is focused on strategic and business model innovation.

By attending this masterclass, participants will
- Explore NEW BUSINESS OPPORTUNITIES;
- NETWORK with top executives;
- Develop a CREATIVE BUSINESS STRATEGY;
- Learn to FORESEE BUSINESS TRENDS;
- Generate EFFICIENT BUSINESS MODELS;
- Explore how DISRUPTION CAN DEVELOP their industries;
- Learn to ADAPT in a volatile business ecosystem.
Business Strategy and Innovation are the answer for Successful Top Executives
The pandemic is the most disruptive event in modern history taking an unprecedented toll on the business environment.
It has presented top executives in every industry with new challenges ranging from team management to customer behavior changes, business operations to company culture.
When disruption occurs to such an extent, business executives need to take action.
How can businesses protect themselves against disruption?
By designing a new business strategy and a company culture that encourages innovation.
Why is business strategy important?
Because strategy drives decisions in business. The strategy provides the organization with the most effective path and direction to achieve its goals.
Why is innovation essential for business?
Because innovation helps businesses grow. Organizations that are continually innovating are more likely to achieve competitive advantage.
Set your business for success and attend BRAND MINDS’ Business Strategy for Top Executives Masterclass!
Join the Conversation
We’d love to hear what you have to say.
Get in touch with us on our LinkedIn Page, Facebook Page, Twitter or TikTok.
20 essential KPIs you should be tracking to improve your marketing (updated for 2021) Part 1
Looking to learn about KPIs and how you can use them to improve your marketing? Then this article is for you!
- What is a KPI in marketing?
- KPIs vs marketing metrics
- How are KPIs used to measure performance in marketing?
- 20 examples of essential KPIs for marketing
What is a KPI in marketing?
KPI stands for key performance indicator.
A KPI in marketing is a measurable value tied to specific objectives of a marketing campaign.
KPIs help measure marketing effectiveness at the end of a campaign.
KPIs vs marketing metrics
Isn’t KPI the same as marketing metrics?
No, it’s not and you must be able to know the difference between KPIs and marketing metrics.
Marketing metrics are measurable values that include everything from the number of followers of the brand’s page on Facebook, Instagram, YouTube, TikTok to website traffic, email subscribers, MQL (marketing qualified leads) and the list can continue. It’s everything you can measure at any given time.
The KPI belongs to the marketing metrics category, it is indeed a marketing metric itself.
The difference is that the KPIs are tied to a specific goal of a specific marketing campaign whereas marketing metrics are not tied to a specific goal of a specific marketing campaign.
Every marketing campaign has one or several marketing goals. To measure how effective your campaign was to achieve your goals, select the appropriate KPIs.
How are KPIs used to measure performance in marketing?
Before we talk about how to use KPIs to measure and track performance in marketing campaigns, it’s essential to understand the brand’s business goals and objectives.
You cannot measure progress if you don’t know what progress looks like. Or what success means for your business.
So, if you are the leader of your team, share the brand’s business goals for 2021 with your colleagues.
They could focus on revenue (increase sales), suppliers (replace old suppliers with new, more performant ones), employees (reduce employee turnover), profit (increase profit margin) or market (increase market share).
Once everyone in your team is aware of the business goals they need to achieve, you can move on to the next step: establishing marketing goals.
Here are some of the common marketing goals:
- Increase Brand Awareness
- Lead generation
- Promote new products/services
- Target new customers
- Increase website traffic
- Grow your email list
If your business goal is to increase revenue, what marketing campaigns your team needs to create and run in order to achieve it?
You could consider implementing several marketing campaigns. For example, a marketing campaign targeted at new customers or a marketing campaign targeted at your current customers with the goal of upscaling. What would you like them to do: buy more in quantity or buy products that are more expensive?
The KPIs tied to this particular marketing campaign could be 20% new leads generated or 20% customer conversion rate.
20 examples of essential KPIs for marketing
Here are 20 essential KPIs that you should track to measure your marketing performance:
- Email open rates
- Email click-through rates
- Email forward rates
- Newsletter signup conversion rate
- Social media engagement rate
- Social media conversions
- New leads generated
- Cost per lead
- Customer lifetime value
- Returning website visitors
- Goal completion rate
- Marketing revenue attribution
- Customer acquisition cost (CAC)
- Landing page conversion rates
- Traffic-to-lead ratio
- Lead-to-customer ratio
- Customer retention
- Content downloads
- Referral traffic
- Net promoter score
1. Email open rates
You worked hard to gain new subscribers to the company’s newsletter, but all is in vain if your emails remain unopened. Optimize your headlines. Are you sending too many emails per week? If you do, but your subscribers don’t click the unsubscribe button then they wish to receive your emails but they are too often which leads to fatigue.
2. Email click-through rates
Your subscribers are opening your emails – that’s great! One of your email campaign goals is to drive website traffic so the email clickthrough rate is an important KPI. If you note this particular indicator is unsatisfactory (what value did you set for email clickthrough rates?) because the subscribers are not clicking on the links, you should consider the content and the copy. Is the linked content relevant to subscribers? Re-write the copy: don’t use learn more to persuade the subscriber to click the link. Get creative!
3. Email forward rates
The email forward rate is one of the most important KPIs if you are looking to grow a community for the brand. Opening the email and clicking on the content links inside is one thing, but making your message so relevant to your subscribers that they forward it to someone else is a great achievement.
4. Newsletter signup conversion rate
How many people did your email subscribing campaign convert? This KPI shows how well you were able to find a match between the brand’s offering and their interests, to speak to their values and show them your solution to their pain points.
5. Social media engagement rate
They say liking a post is the easiest engagement action that your followers can take whereas commenting is the hardest. Having followers that take the time to express their opinion in a comment to your post is more valuable than receiving likes. It also tells the algorithm that this piece of content is sparking conversations which prompts it to show your post to more people.
6. Social media conversions
It’s nice to have a big number of followers on social media accounts, preferably in the millions. It is an indicator that the brand is popular and a lot of people want to stay connected with the brand. After having said that, let’s also not forget that the algorithm shows your content to a small number of people. Some say it’s 1% or 2%. So this vanity metric is a nice-to-have feature, but it is not essential. What is instead relevant is how many conversions does your social content drive? How many clicks to website? How many email subscribers? How many leads does it generate?
7. New leads generated
Generating new leads is paramount for every brand. You need to constantly show your products or services to new leads gently nudging them to the next step in your marketing and sales funnel.
8. Cost per lead
Lead generation is important, but if the cost of acquiring leads is high, you need to take a step back, analyze every stage of the process and see where you can improve it. The Pirate Funnel may help you pinpoint where your business is losing customers. Check it out!
9. Customer lifetime value
Customer lifetime value is the total revenue you can expect from a customer during the period that they remain a customer. Or simply put: how much are they worth to your brand? For example, Amazon Prime members are worth twice as much as non-Prime shoppers. Prime shoppers spend $1,340 annually, more than twice as much as non-Prime shoppers, who spend $650 annually.
10. Returning website visitors
Having a good amount of website traffic is necessary if you want to run ads, show up in organic search results and gain email subscribers. Your website is owned media, it’s where you control the content – your brand is not at the mercy of any social media algorithms. It’s important to measure the number of new visitors your website gets every month. But equally important is to track how many visitors return to your site. Returning visitors tell you that your website is a relevant and valuable resource for them. It’s how your brand stays top of mind. It’s also easier to convert returning visitors to leads and then customers.
Join the Conversation
We’d love to hear what you have to say.
Get in touch with us on our LinkedIn Page, Facebook Page, Twitter or TikTok.
4 lessons in leadership from Hamilton: An American Musical
Hamilton is the latest hit in musicals which has rapidly grown to a pop culture status. Read on to learn 4 lessons in leadership from Hamilton: An American Musical.
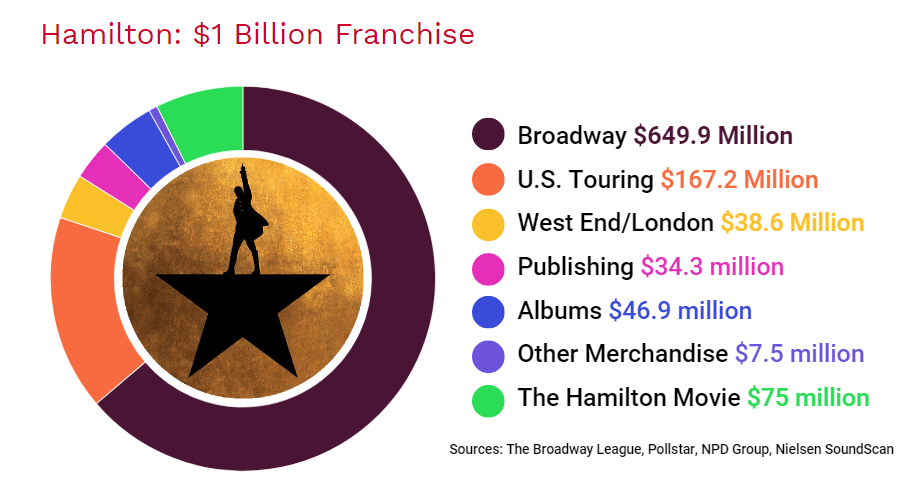
Hamilton, the cultural phenomenon surpassed $1 billion in global sales
Hamilton: An American Musical made its Broadway debut six years ago and it has already become one of the most popular musicals of all time.
In 2016, the show won 11 Tony Awards, the Grammy for best musical theatre album and the Pulitzer Prize for Drama.
The Hamilton music is a wonderful combination of rap, hip-hop and R&B raising the bar for every actor in the show and setting records. Because it’s rap and hip-hop, Hamilton packs the highest number of words per minute than any other musical: 144 with a total word count of 20,520. The runner-up, Phantom of the Opera had 77 words per minute and a total of 4,709 words. The music literally takes your breath away!
Tickets sell out almost instantly. Hamilton is a smashing hit with fans of all ages and all over the world. Just browse the content on the musical’s social accounts (followed by 4,450,000 million people combined, btw!) and see for yourself.
Disney+ has contributed to Hamilton’s global success by bringing the acclaimed musical to the small screen. The Hamilton Movie premiered on Disney+ streaming service last year, in July. It was a good business decision for Disney+ also: the musical spurred a 74% spike in downloads.
4 lessons in leadership from Hamilton: An American Musical
Hamilton tells the story of Alexander Hamilton, one of the Founding Fathers of the United States of America.
The story, music and lyrics were written by actor and Tony winner Lin-Manuel Miranda and is narrated by Aaron Burr, a contemporary of Hamilton and the third vice president of the United States.
Who is Alexander Hamilton?
Alexander was an immigrant from the Caribbean who raised himself from poverty.
He was born out of wedlock and became an orphan as a child. He was driven by ambition, had a remarkably sharp mind and rhetorical skills.
When he was in his early 20s, Alexander became George Washington’s right-hand man during the American Revolutionary War.
Later he was appointed the 1st U.S. secretary of the treasury. He played a key role in defending and ratifying the U.S. Constitution and was the chief architect of the American financial system.
Here’s what the leaders of the 21st century can learn from the 18th-century leader, Alexander Hamilton:
- Make self-growth a goal for you and your team;
- Develop partnerships;
- Tell the world what you believe in and stand by your beliefs;
- Communicate your ideas.
Lesson #1: Make self-growth a goal for yourself and your team
Alexander Hamilton is a unique figure among the other Founding Fathers of America. His family was not wealthy and didn’t have any titles. He was so poor that he couldn’t afford to go to any regular schools. Because he was an illegitimate child, Alexander was also denied access to church schools.
But he was an avid reader. What he couldn’t learn in school, he learned by himself.
By the age of 15, he had already developed a talent for mathematics and business working as a clerk for a local successful merchant.
He could also write extremely well for his age which helped him stand out in his community.
Helped by his employer, Alexander enrolled in King’s College (later renamed Columbia University) at 16 where he was granted independent study. This allowed Alexander to move through his courses quickly, often hiring college professors to provide him with personal instruction outside of regular class hours. He also became fluent in French which would give him an advantage during the American Revolution.
After the war, he studied law to pass the bar exam and become a lawyer. He didn’t go to law school, he studied independently for ten months before passing the exam with flying colours.
Hamilton was an ambitious young man who learned very early in his life that acquiring knowledge and developing one’s skills and abilities was paramount to being fulfilled and successful.

Scene from Hamilton, the musical
No matter your life situation, expanding your knowledge in the areas of your interest is essential to your success.
Young or old, learning never stops. Go deeper on the topic of your choosing. Or start afresh on a new path towards a different interest that you always wished you could explore but never found the time.
Now is the time to begin. Pick up a book and become a self-taught leader. Or enroll in an online class.
If you are looking to learn the principles of innovative companies, attend BRAND MINDS’ Business Strategy Masterclass for Top Executives with London Business School professor Costas Markides.
The masterclass takes place online, on the 23rd of March, 2021. You will learn how to develop custom business models and business strategies for your company. Learn more about the masterclass.
A successful leader seeks opportunities to grow not only himself but his team too. Because a leader’s main responsibility is to grow other leaders. So consider attending our business masterclass with your team. Check our discounts for team growth.
Lesson #2: Develop and maintain partnerships
The musical depicts the strong bond between Hamilton and several influential figures, including spy Hercules Mulligan, the anti-slavery John Laurens, the French revolutionary Marquis de Lafayette and commander-in-chief and later the first President of the United States George Washington.
Hamilton became friends with Mulligan, Laurens and Lafayette. They shared the same values, supported each other and became close during the war. Their leadership, resourcefulness, and courage helped secure the American victory with the British.
A young captain in the army, Hamilton demonstrated superior command of administrative and logistical matters which soon brought him to the attention of General George Washington. The general invited him to become one of his aides and Alexander accepted the offer. He remained on Washington’s staff for four years forming a strong and lasting friendship with the general, who relied on him heavily. It was also a mentorship relationship, one which helped Hamilton acquire leadership skills.
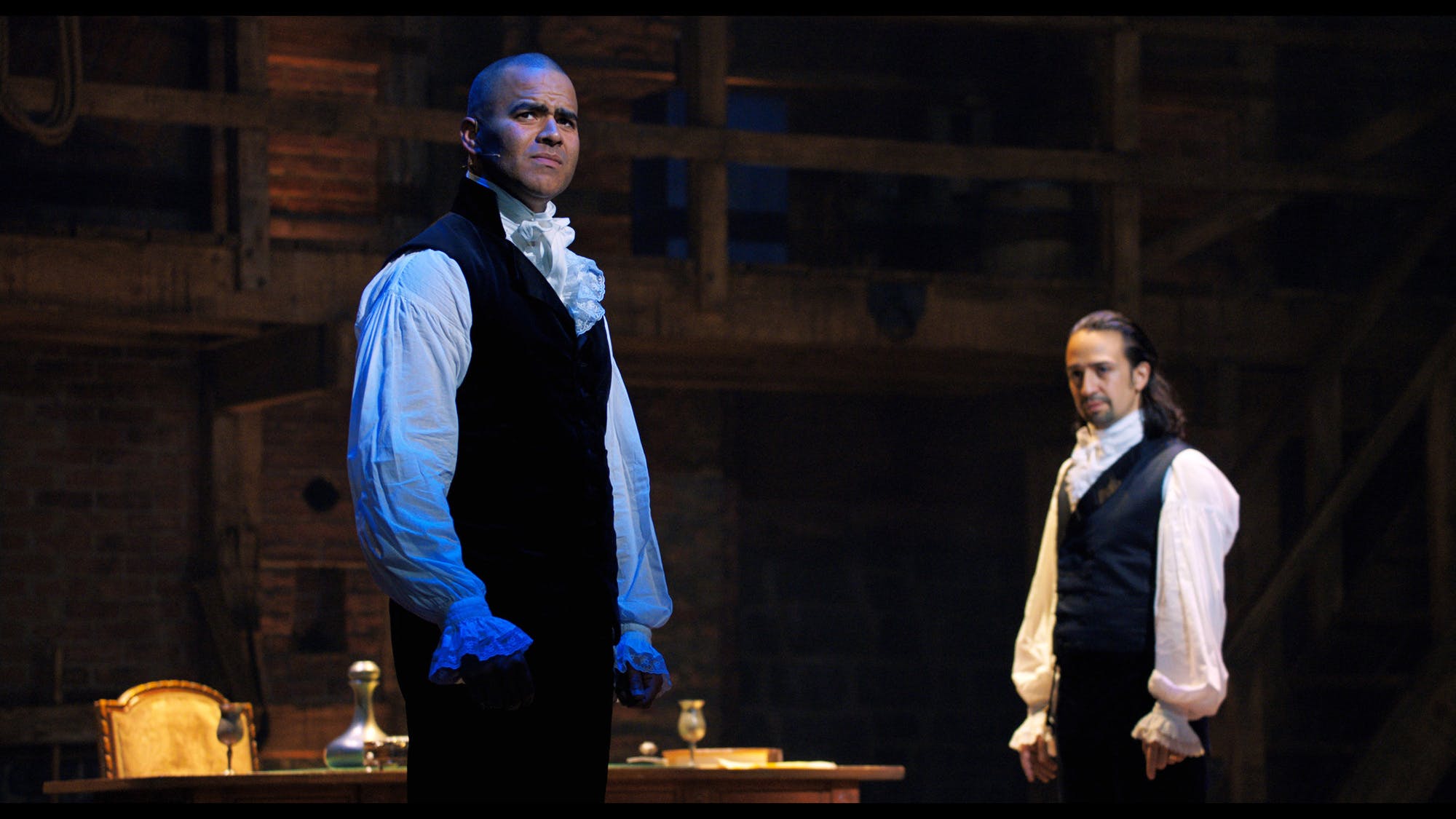

Scene from the musical: General George Washington and his right-hand man, Alexander Hamilton
Aside from a close-knit team, a leader needs partners, people who share the same values and who work together to achieve a common goal. It takes a lot of work and trust to build a valuable partnership. Both partners must deliver on their word and support each other through thick and thin.
Look for partners that can build you up. Develop close relationships with people that you can learn from. Seek and offer support to your partners when they need it. Let them know that you will be there for them. And they will be there for you.
Lesson #3: Tell the world what you believe in and stand by your beliefs
Hamilton had strong beliefs and didn’t shy away from making them known to whoever was willing to listen.
Thanks to his rhetorical abilities, it was easy for him to step on a chair and convey his ideas to the audience with confidence and ambition.
Here is the scene where Laurens, Madison and Lafayette notice Alexander’s talent and gently encourage him to the forefront – “let’s get this guy in front of a crowd”.

Scene from the musical: Alexander Hamilton (front) with Laurens, Madison and Lafayette
What are your core values and purpose? Talk about them, share them with your employees, partners, clients and suppliers.
Today a company employing thousands of people all over the world has this in common with a company with just twenty employees – they both stand for something.
Walmart, Disney and L’Oreal have announced their commitments to a zero deforestation policy, an initiative that ensures companies make their products without destroying the world’s forests.
Atlassian, Dropbox and Accenture champion diversity and foster a culture of inclusivity.
And then you have small companies or startups that are built around sustainability and diversity from the get-go. Ecoalf is a Spanish company that turns plastic sea waste into high-quality fashion products. Danish company Matter assists its clients to choose a sustainable pension, namely the company makes sure that its clients invest their pensions in companies that have a positive impact on the world.
When the business is built on a purpose with positive social and environmental impact, it differentiates itself from the competition. Having a brand purpose that customers care about has been reported to influence the brand’s revenue.
Accenture’s latest annual Global Consumer Pulse Research found that 62 per cent of customers want companies to take a stand on current and broadly relevant issues like sustainability, transparency or fair employment practices.
Unilever is a good example of how focusing on sustainability drives revenue. Nearly half of its top 40 brands focus on sustainability with Knorr, Dove and Lipton among them. According to the report, these brands grow 50 per cent faster than the company’s other brands and deliver more than 60 per cent of the company’s growth.
Making your beliefs known is also beneficial to your personal brand in that it opens up various opportunities for projects or support that you couldn’t get otherwise. Instead of going to people, people come to you.
In the musical, Aaron Burr is the opposite of Hamilton. He believes that revealing his views on topics of the highest importance makes him vulnerable, effectively handing his enemies the bullet with which to kill him. One of his recommendations to Alexander starting out his life in New York is to “talk less, smile more and don’t let them know what you’re against or what you’re for”.
That strategy didn’t play out well for Aaron when he ran against Thomas Jefferson for the presidency of the United States years later, in 1800. With both candidates at a tie, Hamilton was called upon to announce which candidate claimed his vote. Although he didn’t agree with Jefferson on many subjects, Hamilton votes for him because “when all is said and all is done, Jefferson has beliefs, Burr has none!”
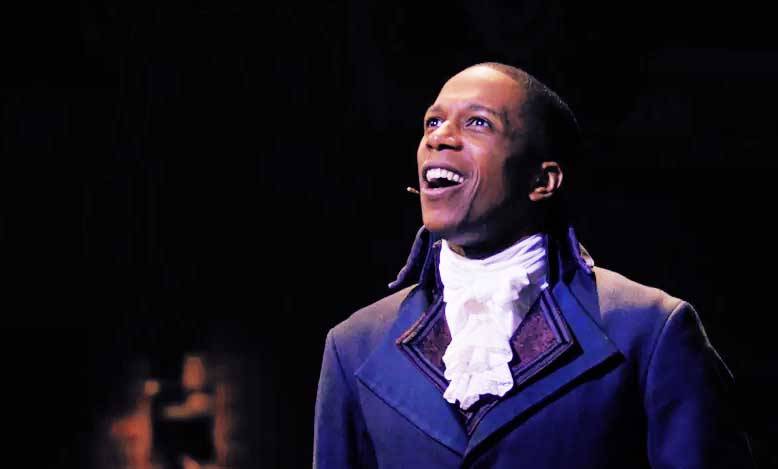

Scene from the musical: Aaron Burr played by Leslie Odom Jr
Lesson #4: Communicate your ideas, beliefs and purpose
As you learned at #1, Alexander was quite the writer. When he was a teenager, he published several letters and poetry in his local newspaper that made him famous in his community.
Later on, among his duties as Washington’s right-hand man was writing letters for the General.
While studying for his bar exam, Alexander published a book called Practical Proceedings in the Supreme Court of New York which compiled his analysis of old New York court cases. The book became a manual in New York legal studies for decades afterwards.
To convince the people that the Constitution was essential to their liberty, Hamilton decided to write a series of essays. He enlisted John Jay and James Madison to assist him in writing the essays. The three men published 85 essays which became collectively known as the Federalist Papers of which Hamilton wrote 52.
How did Hamilton write? Paraphrasing the Non-stop song: Hamilton wrote day and night like he was running out of time, like tomorrow won’t arrive, as he needed it to survive.

Excerpt from the Non-stop scene
If you’re leading a company, people want to hear from you. If you’re leading a team, the team members want to hear from you.
You have a unique perspective on business and life. What are your challenges? What are your successes? What are your aspirations? What inspires and motivates you? People want to learn about other people’s experiences.
Today there are many ways leaders can communicate their ideas, beliefs and purpose. If you’re good with writing words on paper, start a blog. If you’re a good speaker, start a podcast or YouTube channel. Go live on Facebook or LinkedIn.
Bill Gates writes on Gates Notes, his blog and has just started hosting a podcast series with co-host actress Rashida Jones. Former Disney CEO Robert Iger wrote a book. And I could go on with many other examples.
The tools are readily available, all you need is a simple strategy and the time to implement it.
Join the Conversation
We’d love to hear what you have to say.
Get in touch with us on our LinkedIn Page, Facebook Page, Twitter or TikTok.
Alexander Hamilton biography source: SparkNotes
How Amazon, Nike and UiPath drive innovation
Innovation is at the core of Amazon, UiPath and Nike. Curious to know how these global companies drive innovation? Keep reading!
Amazon – Innovating by focusing on customer needs like no other company in the world
On December 15, 2020, Amazon announced that Twitter has selected AWS to provide global cloud infrastructure to deliver Twitter timelines.
A day before, Amazon launched Alexa’s new Live Translation feature. This feature allows individuals speaking in two different languages to converse with each other, with Alexa acting as an interpreter and translating both sides of the conversation.
Earlier this month, on December 8, 2020, Amazon Web Services (AWS) and the BMW Group announced a comprehensive strategic collaboration to further accelerate the automaker’s pace of innovation by placing data and analytics at the center of its decision-making.
These are just a few of the innovations that Amazon releases on a monthly basis. Amazon began focusing on technology innovations in the late 1990s.
The company’s first major breakthrough was its recommendation algorithm, also named recommendation engine.
In 2003, Amazon published a research paper which described a new way of filtering, the Item-to-item Collaborative Filtering.
“At Amazon.com, we use recommendation algorithms to personalize the online store for each customer. The store radically changes based on customer interests, showing programming titles to a software engineer and baby toys to a new mother”, was said in the paper.
Today, Amazon’s machine learning-powered recommendation engine drives 35% of its sales according to a McKinsey report.
An online bookstore initially, Amazon has become rapidly aware of the necessity of becoming a tech company.
In 2019, the research and development expenses of Amazon were around $36 billion compared to $16.9 billion of Microsoft.
Amazon’s investment supports the company to achieve its vision of becoming “Earth’s most customer-centric company.”
Here is a list of the most important innovations developed by Amazon:
Amazon Go
Amazon Go is a chain of convenience stores in the United States, operated by Amazon. The stores are partially automated, with customers able to purchase products without being checked out by a cashier or using a self-checkout station. There are currently 27 Amazon Go stores.
Amazon fulfillment centers
In every fulfilment centre, computer vision systems analyze images to help Amazon staff keep track of everything. Based on data, AI solves a large combinatorial optimization problem and decides which orders to pick at the same time in order to get them in the same box. This way the system minimizes the distance the transport pods have to travel. AI optimization makes these decisions in real-time and with information that is constantly changing.
Amazon Prime Now
Amazon Prime Now is an app which allows users to order tens of thousands of products to their homes with 1-hour delivery and FREE 2-hour delivery.
Amazon Prime Air
Amazon Prime Air is a service that will deliver packages up to five pounds in 30 minutes or less using small drones.
AWS – Amazon Web Services (AWS) is the world’s most comprehensive and broadly adopted cloud platform, offering over 175 fully featured services from data centers globally. The platform is used by individuals, companies, and governments, on a metered pay-as-you-go basis.
Alexa
Alexa is a virtual assistant AI technology developed by Amazon in 2014 and first used in the Amazon Echo smart speakers.
Kindle
Kindle is a series of e-readers which enable users to browse, buy, download, and read e-books, newspapers, magazines and other digital media. The device was launched in 2007.
Style Snap
StyleSnap is the latest Amazon AI-powered feature which supports fashion-focused shoppers.
Show and Tell
Show and Tell allows the blind to identify grocery items by holding each item to the Echo Show camera and ask, “Alexa, what am I holding?”. The smart speaker identifies the item through advanced computer vision and machine learning technologies for object recognition.
UiPath – The path to innovation is paved with humility
UiPath is the world’s leading Robotic Process Automation vendor.
For the second consecutive year, UiPath has been placed highest in the Leaders’ quadrant for ability to execute by Gartner.
In July 2020, UiPath became the first European Cloud Decacorn with $10.2Bn valuation in a new funding round of $225M.
At UiPath, innovation comes from actively listening to and engaging with the company’s customers. “Solving real-world problems using artificial intelligence (AI)—and pairing AI with RPA—motivates every individual at UiPath.”
The company gathers feedback from many touchpoints, including preview programs, its customer advisory board, their 400k+ user community, meetups, and conferences.
UiPath’s purpose is to accelerate human achievement. The company’s core values are speed, immersion, boldness and humility.
UiPath top management believes that if their people are not happy, they have failed no matter how successful the company is. That’s why being a successful leader at UiPath means exercising humility and practising active listening. The employee who is provided with psychological safety is more likely to focus on achieving the company’s business goals.
Nike – Innovation through knowledge and insights
Nike is no longer just an athletic shoe manufacturer, it’s a technology company.
The brand’s mission is to expand human potential. And to achieve that, Nike creates new products through game-changing innovations.
Most innovations come from the brand’s own lab, the Nike Sport Research Lab which the company set up in 1980. The lab focuses on biomechanics, physiology, sensory/perception and data science.
Over the course of thirty years, Nike’s lab, employing more than 40 researchers has grown into a world-class research facility. Its function is to provide knowledge and insights and turn data into innovative products for athletes.
The Nike Flywire support system, Lunarlite foam cushioning, Hyperdunk basketball shoe are among the most famous.
The latest innovation is Nike Fit, a foot-scanning solution designed to find every person’s best fit. Nike Fit uses a proprietary combination of computer vision, data science, machine learning, artificial intelligence and recommendation algorithms to find your right fit.
A report from 2017 estimated that Nike has spent “~$2.5 billion on research and development in the last five years.”
Read BUSINESS reSOURCES: a PESTEL analysis of Nike
Join the Conversation
We’d love to hear what you have to say.
Get in touch with us on our LinkedIn Page, Facebook Page, Twitter or TikTok.
5 steps to create a strategic plan that will support your business vision
In this article:
-
What is strategic planning in business: definition of the strategic plan, who creates a strategic plan, the main goal of a strategic plan;
-
Strategic plan vs Business plan;
-
Benefits of strategic planning;
-
The strategic planning process: 5 steps to create a strategic plan that will support your business vision.
1. What is strategic planning in business?
Strategic planning is an organizational management activity. The company’s CEO and senior leadership team are tasked with creating a strategic plan, it’s one of their responsibilities.
The goal of a strategic plan is to provide you with a roadmap to align the organization’s functional activities to achieve set goals and determine the direction in which you want to take your business.
The plan outlines what (resources), how (specific tools, activities, platforms etc) and why (the reasons behind your choice of a specific resource or tool) the company will use to achieve its goals.
The main goal of your strategic plan is differentiation
The main goal of the strategic plan you create for your business is to define how your business differentiates itself from the competition.
What activities is your business performing that are different from the activities performed by your competitors?. Or what activities that are similar to your competitors’ you perform differently?
Harvard professor and author of Porter’s 5 Forces Michael Porter defines strategy as “performing different activities from others or performing similar activities in a different manner.”
Nikki Reed’s jewellery – a case study on business differentiation
Twilight series actress Nikki Reed designs beautiful jewellery. Her collections include 14-18 karat gold pieces. As opposed to other jewellery designers, her collections are made from e-waste.
Nikki’s business goal is to produce jewellery that is ethically made, sustainable and chemical-free. To achieve her goal, she partnered with computer technology company Dell.
According to the latest stats, it is estimated that our smartphones contain more than $60 million in gold and/or silver which are thrown away every year. Dell has developed a process for extracting gold from old computer motherboards that is 99% more environmentally friendly than extracting gold from the earth.
That’s how Nikki Reed differentiates her business from competitors: by using gold responsibly extracted from recovered technology to make beautiful jewellery. See her collections.
2. Strategic plan vs Business plan
A strategic plan is for established businesses looking to grow by providing them with focus, direction and action. Whereas a business plan is for businesses starting out and provides the entrepreneur with a structure for his ideas defining the business.
A strategic plan generally covers a period of 3 to 5+ years, whereas a business plan is normally no more than one year.
Discover more differences between a strategic plan and a business plan.
3. Benefits of strategic planning
No matter how much you wished your business had no competition on the market, your competitors are not going away just because you wish them to.
What you could do, after a thorough analysis of your business, the market and your competition is to devise a strategy that would help your business achieve its goals by doing things differently.
By having a strategic plan in place the top management conveys trust to the company’s employees.
A clear path to achieving set business goals means the team is more likely to enjoy an increased level of focus, determination and creativity.
Success is more easily achievable when everyone knows what to do and how to do it.
4. The strategic planning process
Before going into the strategic planning process, the CEO and top management have to be clear on the company’s vision, mission and organizational goals and objectives.
The CEO or founder is responsible for creating the vision and formulating the mission. The business vision states why you do it while the business mission states what your company does to achieve its vision.
The vision statement provides a snapshot of what the world would look like as a result of the company’s services. The mission statement is the roadmap for the company’s vision statement.
Let’s look at the vision and mission statements of a number of companies whose products and services you might use on a daily basis.
Vision – To provide access to the world’s information in one click.
Mission – Our mission is to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.
AMAZON
Vision – We aim to be Earth’s most customer-centric company.
Mission – Our mission is to continually raise the bar of the customer experience by using the internet and technology to help consumers find, discover and buy anything, and empower businesses and content creators to maximize their success.
SALESFORCE
Vision – Salesforce is the world’s #1 customer relationship management (CRM) platform.
Mission – We bring companies and customers together. We help your marketing, sales, commerce, service and IT teams work as one from anywhere — so you can keep your customers happy everywhere.
Did you know? SalesForce has recently announced that it will acquire Slack for $27.7 billion.
TIKTOK
Vision – TikTok is the leading destination for short-form mobile video.
Mission – Our mission is to inspire creativity and bring joy.
5 steps to create a strategic plan that will support your business vision
A company’s vision and mission are not set in stone. Your business may transform as a result of technological developments or customer behaviour changes. For this reason, it is important to revisit the company’s vision and mission and amend them if necessary.
- Market analysis
- Development
- Implementation
- Review and update
- Evaluation and measurement
Step 1 – Market analysis
Before anything else, it is important to get updated on the current status of your business.
Perform a SWOT analysis to see if there are changes in your company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats?
Are there new threats looming over the business ushered in by the pandemic?
Can you turn a new threat into an opportunity?
How is the pandemic affecting your bottom line?
Next, apply PORTER’s 5 Forces framework to your industry to evaluate how the pandemic is influencing the drivers of profitability and competition in your market. Get your team together and discuss what valuable insights you can take away from this analysis. How could these insights help you come up with a specific and unique way in which to delight your customers today?
PESTEL is another great tool that you can use to understand the impact of macro-environmental factors on your business. The PESTEL acronym stands for Political, Economical, Social, Technological, Environmental and Legal.
How are these factors that you cannot influence, affecting your business?
Check out a PESTEL analysis of Nike
Once you have drawn relevant insights from your company and business market analysis, you can move to step 2 of the strategic plan: development.
Step 2 – Development
Sit down together with your team and write the strategic plan.
Include the following:
- Company description
- Mission, vision and value statements
- Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats
- Describe the current drivers of profitability and competition (PORTER’s 5 Forces)
- Describe how the macro-environmental factors impact your business (PESTEL)
- Prioritize your objectives
- Determine your strategic position (ie: at least one way in which your business will differentiate itself from the competition)
- Describe in great detail how you are going to leverage your newly developed strategy to achieve your business goals (means of communication, resources, budget etc)
- Include an execution timeline and how you are going to measure success
- Review and revise the plan.
Step 3 – Implementation
Now that you have the strategic plan on paper it’s time to execute it.
But before that, you need to communicate your plan to the employees that are going to implement it.
Choose the best way to do that. Is it a lengthy email? Or an all-hands meeting?
Prepare yourself to answer questions and convey your vision as clearly as possible.
You might also need to provide inspiration and motivation.
Step 4 – Review and Update
Determine when to review the strategic plan over the course of the implementation and go back to the plan to update it if necessary: 3 months? 6 months?
Step 5 – Evaluation and measurement
Once the strategic plan has been executed, it’s time for evaluation and measurement.
Extract the results and measure them against your set projections.
Calculate the KPIs and ROI.
Did the strategic plan help your business to achieve its set objectives?
Join the Conversation
We’d love to hear what you have to say.
Get in touch with us on our LinkedIn Page, Facebook Page, Twitter or TikTok.
March 2021: Business Strategy Masterclass for Top Executives with Prof. Costas Markides
Dear world-changer,
We have exciting news!
BRAND MINDS is launching Business Strategy Masterclass for Top Executives with London Business School professor Costas Markides.
The masterclass is scheduled for March 23rd, 2021 and will take place online. It starts at 9 am and ends at 5 pm with a Q&A session which is a great opportunity to get answers to your questions.
Check the agenda to find what you will learn at this masterclass:
Session 1: Strategy in a volatile world
Session 2: Strategic agility in today’s world
Session 3: Mobilizing the whole organisation for strategy execution
Session 4: New challenges for leaders
6 benefits of attending Business Strategy Masterclass for Top Executives
![]() BUILD CUSTOM BUSINESS MODELS
BUILD CUSTOM BUSINESS MODELS
Learn to develop custom business models and drive success through innovation.
![]() WORLD-CLASS EXECUTIVE EDUCATION
WORLD-CLASS EXECUTIVE EDUCATION
Acquire a premium learning experience from the former Executive Education Director of London Business School.
![]() EXPAND YOUR COMPANY
EXPAND YOUR COMPANY
Drive growth by exploring new business opportunities through networking with other Top Executive participants.
![]() BECOME THE ARCHITECT OF YOUR BUSINESS
BECOME THE ARCHITECT OF YOUR BUSINESS
Acquire the necessary business tools to plan your company’s future efficiently.
![]() LEARN BUSINESS INNOVATION PRINCIPLES
LEARN BUSINESS INNOVATION PRINCIPLES
Upgrade your knowledge on innovation and disruption to drive business success.
![]() IMPROVE YOUR DECISION-MAKING PROCESS
IMPROVE YOUR DECISION-MAKING PROCESS
In today’s fast-paced environment, making good decisions fast is an invaluable skill.
Are you a CEO, investor, business owner, sales expert, marketing manager, HR director or strategy specialist?
Then this masterclass is for you!
Discover additional benefits for you and your business

Prof Costas Markides – One of the world’s foremost experts on strategy & innovation
A business author and strategic thinker, Costas Markides has been a professor at London Business School for the past 30 years teaching Strategy & Entrepreneurship.
As the holder of the Robert P. Bauman Chair of Strategic Leadership at London Business School, Costas Markides’ role is to create innovative educational approaches that shape the next generation of strategic leaders.
He received his MBA and DBA from Harvard Business School and served as the Faculty Director of Executive Education at London Business School until 2016.
His expertise includes strategic innovation, business model innovation, diversification and international acquisitions.
A skilful professor, he won 5 awards recognizing his excellence in teaching and innovation in learning over the past ten years.
He is the bestselling author of Fast Second: How Smart Companies Bypass Radical Innovation to Enter and Dominate New Markets and Game-Changing Strategies: How to Create New Market Space in Established Industries by Breaking the Rules.

Fast Second illustrates how to determine which new markets have the potential to be successful and how to move into them before the competition does, when to make a move into a new market, how to scale up a market, where to position a company in the market, and whether to be a colonizer or a consolidator.

Game-Changing Strategies presents practical ideas on how established firms could not only discover new radical business models but also grow them next to their existing business models.
His forthcoming book is entitled Architects of Change and is set to launch in April 2021. The new book explores how individuals could design innovative solutions to social problems in ways that make them easily scalable.
Costas is currently serving on several editorial boards of strategic management journals among which is Sloan Management Review, the research-based magazine published at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
Have a long term strategy, especially in a fast-changing world; listen to the customer, but don’t always do what they say; don’t feel threatened by disruptive innovation; promote innovation in the face of core resistance; and, finally, do your best to bridge the know-do gap.
COSTAS MARKIDES
Do you want to get your company ready for an amazing 2021?
Access now BRAND MINDS Business Strategy Masterclass for Top Executives with prof Costas Markides!
Join the Conversation
We’d love to hear what you have to say.
Get in touch with us on our LinkedIn Page, Facebook Page, Twitter, TikTok or YouTube.
BUSINESS reSOURCES: a PESTEL analysis of Nike
A PESTEL analysis of NIKE: learn how the brand’s business is affected by the industry’s macro-environmental factors.
PESTEL business analysis is a framework for helping entrepreneurs and business people to understand the impact of macro-environmental factors on their business.
The PESTEL acronym stands for Political, Economical, Social, Technological, Environmental and Legal. Learn about PESTEL and how this framework can help your business here.
NIKE is the world’s largest athletic shoe manufacturer. Industry experts estimate that the company currently has a 28% share of the market. In 2020, its global revenue amounted to about 37.4 billion U.S. dollars in 2020. If you want to know more about what contributed to the success of one of the most valuable brands in the world, read The story behind the brand: NIKE.
Let’s analyze Nike’s macro-environment by applying the PESTEL framework.
NIKE – Political factors
The political factors help the entrepreneur appraise the degree to which a government intervenes in the economy or a certain industry and how its decisions affect the present and the future of the company.
Overall, the US government has developed many initiatives centred on growth. The United States is a core market for Nike, with the company generating approximately 41% of its overall revenue there in 2019.
Nike shoes are manufactured in 36 factories in the US by 5151 workers. In order to expand to other markets and other business reasons, Nike has 517 manufacturing facilities in 41 countries.
The company has the most manufacturing sites in China and Vietnam (108) followed by Indonesia and Thailand. China is one of the largest markets for Nike with revenues growing 22% in 2019.
As an international company, Nike has to take into account the tariffs that its shoes and other goods are subject to. In the US, for example, the shoe companies pay as much as 25% in tariffs, one of the highest duties compared to other industries.
In 2019, the U.S.-China trade tensions had begun to escalate when Trump threatened to increase tariffs on Chinese goods — including all types of footwear, from sneakers to sandals by 10%. It was estimated that the tariffs would cost American customers an additional $7 billion per year.
In an open letter to Trump, Nike and other 173 footwear companies urged the former President to reconsider his tariffs on shoes made in China and “bring this trade war to an end.”
Industry experts argued that the company would have been affected by the increase in tariffs in a small degree since only 10% of Nike goods produced in China are exported to the American market.
Also, it has diversified its supply chain to include manufacturing sites spread in other countries on the Asian continent like Vietnam, Indonesia and Thailand. That was a good business decision that has shielded the giant shoe producer against the financial consequences of political power.
Nike’s solution: a geographically diverse supply chain.
NIKE – Economical factors
In PESTEL’s analysis, the economical factors determine the economy’s performance by examining economic growth, exchange rates, interest rates, unemployment rates, the state of the country’s infrastructure, taxes.
This factor affects the purchasing power of customers and could change the demand and supply dynamics of the market. Which, in turn, affects the prices of products and services.
Did the 2008 economical crisis affect the giant sportswear?
Yes, it did. Customers were struggling with job loss and falling incomes which lead to a 12% drop in sales. Also, the company’s stock lost as much as 28%.
Nike has adapted to the new environment, by undergoing a costly restructuring cutting costs and 5% of its workforce, in the biggest job reduction in the company’s history. While other businesses went bankrupt, Nike survived.
Once the recession was over, sales and stock recovered strongly. “During times of economic challenge, consumers will go to brands that they trust and can connect with. We have not seen the economy have a dramatic impact on the sales of our products, not just in the high end, but also in the mid-priced range,” Chief Executive Mark Parker said at the time. “We’re able to accomplish this by staying focused on what we do best – deliver innovative products and experiences that serve athletes, inspire consumers and reward our shareholders.”
It’s the same now, in 2020, when we are going through another economic crisis caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. The company lost sales due to widespread physical store closures with global revenues for the fourth quarter dropping by 38%. This revealed the giant’s reliance on high-street shops and its influence on the business.
To balance out the negative consequences of shops closing down, Nike accelerated the efforts toward its eCommerce business.
The company’s digital sales rose to 30% of overall revenues during the pandemic. New membership registrations among Nike apps more than doubled to 25 million during the period, half of which belonged to women.
Nike realized as early as 2011 that going mobile was mandatory. Since then, the company developed the Nike and SNKRS apps. They are designed to increase the brand’s direct connections to consumers which translates into more sales.
Nike’s solution: an ongoing digital strategy.
NIKE – Social factors
According to PESTEL’s business analysis, by looking at social factors companies are able to analyze the behaviour patterns of customers and create a customer profile as accurate as possible.
Within the footwear market, an interesting culture has been growing since the late 1970s-early 1980s – the sneakerhead culture.
Nike knew who its customers were, what they were about and who they were looking up to. At the time, Michael Jordan was winning every game on the basketball court doing his iconic jump. Every kid around the world had a poster of Michael Jordan in his room.
Nike’s partnership with basketball all-time-star Michael Jordan has contributed to the sneakerhead culture rise and global development. Today the sneaker resale market is estimated to reach $2billion.
Nike is also well aware of the changes taking place in society and how the values of their most important customers transformed over the years. Launching its 2018 Dream Crazy ad, Nike knew it would run into controversy and possible backlash from a certain segment of its customer base. Which it did happen. The company was not concerned because this ad was targeted to a specific customer base with which the brand was looking to nurture and connect.
Nike: reflect your customers’ values and beliefs.
NIKE: Technological factors
Technology is one of the factors disrupting operations across almost every industry.
We’ve talked about how important is digital and mobile to Nike’s ecosystem of sales, marketing and community engagement.
Technological developments have been equally important to the company’s product design and manufacturing. The brand’s mission is to expand human potential. And to achieve that, Nike creates new products through game-changing innovations.
Most innovations come from the brand’s own lab, the Nike Sport Research Lab. The Nike Flywire support system, Lunarlite foam cushioning, Hyperdunk basketball shoe are among the most famous.
The latest innovation is Nike Fit, a foot-scanning solution designed to find every person’s best fit. Nike Fit uses a proprietary combination of computer vision, data science, machine learning, artificial intelligence and recommendation algorithms to find your right fit.
Nike is no longer an athletic shoe manufacturer, it’s a tech company.
NIKE – Environmental factors
As with the technological factor, the environmental factor is today of growing importance. Businesses are now called to account for any negative impact their operations have on the environment. Companies big and small are expected to reduce their carbon footprint, take actions to reduce waste and pollution, and preserve the environment.
Not so long ago, Nike was synonymous with sweatshops and negative impact on the environment.
Over the past twenty years, Nike has made great strides in becoming environmentally conscious and sustainable.
Today Nike pledges to use only renewable energy and reduce its shipping emissions. The company designed a line of sports jerseys and sneakers crafted from recycled waste plastics and announced its commitment to switch to 100% renewable energy by 2025.
Also, by the end of 2021, Nike will completely eradicate single-use plastic bags in all its stores.
Nike: environmentally conscious and sustainable.
NIKE – Legal factors
The legal factor of PESTEL analysis looks into the laws and regulations of the industry.
Over the years, Nike has been in a number of legal battles.
In the late 1980s, the company has been taken to court for failing to disclose poor working conditions.
It also has a long legal history with Adidas over patent infringements.
Recently Nike filed recently filed a lawsuit against footwear rival Skechers for copying design patents.
The global athletic footwear industry is expected to rise to an estimated value of USD 96.10 billion by 2026 so the competition within the market is fierce.
Nike: protects its design patents in court.
Join the Conversation
We’d love to hear what you have to say.
Get in touch with us on our LinkedIn Page, Facebook Page, Twitter or TikTok.



